|
Topics
Introduction
Problems Freedom Knowledge Mind Life Chance Quantum Entanglement Scandals Philosophers Mortimer Adler Rogers Albritton Alexander of Aphrodisias Samuel Alexander William Alston Anaximander G.E.M.Anscombe Anselm Louise Antony Thomas Aquinas Aristotle David Armstrong Harald Atmanspacher Robert Audi Augustine J.L.Austin A.J.Ayer Alexander Bain Mark Balaguer Jeffrey Barrett William Barrett William Belsham Henri Bergson George Berkeley Isaiah Berlin Richard J. Bernstein Bernard Berofsky Robert Bishop Max Black Susan Blackmore Susanne Bobzien Emil du Bois-Reymond Hilary Bok Laurence BonJour George Boole Émile Boutroux Daniel Boyd F.H.Bradley C.D.Broad Michael Burke Jeremy Butterfield Lawrence Cahoone C.A.Campbell Joseph Keim Campbell Rudolf Carnap Carneades Nancy Cartwright Gregg Caruso Ernst Cassirer David Chalmers Roderick Chisholm Chrysippus Cicero Tom Clark Randolph Clarke Samuel Clarke Anthony Collins August Compte Antonella Corradini Diodorus Cronus Jonathan Dancy Donald Davidson Mario De Caro Democritus William Dembski Brendan Dempsey Daniel Dennett Jacques Derrida René Descartes Richard Double Fred Dretske Curt Ducasse John Earman Laura Waddell Ekstrom Epictetus Epicurus Austin Farrer Herbert Feigl Arthur Fine John Martin Fischer Frederic Fitch Owen Flanagan Luciano Floridi Philippa Foot Alfred Fouilleé Harry Frankfurt Richard L. Franklin Bas van Fraassen Michael Frede Gottlob Frege Peter Geach Edmund Gettier Carl Ginet Alvin Goldman Gorgias Nicholas St. John Green Niels Henrik Gregersen H.Paul Grice Ian Hacking Ishtiyaque Haji Stuart Hampshire W.F.R.Hardie Sam Harris William Hasker R.M.Hare Georg W.F. Hegel Martin Heidegger Heraclitus R.E.Hobart Thomas Hobbes David Hodgson Shadsworth Hodgson Baron d'Holbach Ted Honderich Pamela Huby David Hume Ferenc Huoranszki Frank Jackson William James Lord Kames Robert Kane Immanuel Kant Tomis Kapitan Walter Kaufmann Jaegwon Kim William King Hilary Kornblith Christine Korsgaard Saul Kripke Thomas Kuhn Andrea Lavazza James Ladyman Christoph Lehner Keith Lehrer Gottfried Leibniz Jules Lequyer Leucippus Michael Levin Joseph Levine George Henry Lewes C.I.Lewis David Lewis Peter Lipton C. Lloyd Morgan John Locke Michael Lockwood Arthur O. Lovejoy E. Jonathan Lowe John R. Lucas Lucretius Alasdair MacIntyre Ruth Barcan Marcus Tim Maudlin James Martineau Nicholas Maxwell Storrs McCall Hugh McCann Colin McGinn Michael McKenna Brian McLaughlin John McTaggart Paul E. Meehl Uwe Meixner Alfred Mele Trenton Merricks John Stuart Mill Dickinson Miller G.E.Moore Ernest Nagel Thomas Nagel Otto Neurath Friedrich Nietzsche John Norton P.H.Nowell-Smith Robert Nozick William of Ockham Timothy O'Connor Parmenides David F. Pears Charles Sanders Peirce Derk Pereboom Steven Pinker U.T.Place Plato Karl Popper Porphyry Huw Price H.A.Prichard Protagoras Hilary Putnam Willard van Orman Quine Frank Ramsey Ayn Rand Michael Rea Thomas Reid Charles Renouvier Nicholas Rescher C.W.Rietdijk Richard Rorty Josiah Royce Bertrand Russell Paul Russell Gilbert Ryle Jean-Paul Sartre Kenneth Sayre T.M.Scanlon Moritz Schlick John Duns Scotus Albert Schweitzer Arthur Schopenhauer John Searle Wilfrid Sellars David Shiang Alan Sidelle Ted Sider Henry Sidgwick Walter Sinnott-Armstrong Peter Slezak J.J.C.Smart Saul Smilansky Michael Smith Baruch Spinoza L. Susan Stebbing Isabelle Stengers George F. Stout Galen Strawson Peter Strawson Eleonore Stump Francisco Suárez Richard Taylor Kevin Timpe Mark Twain Peter Unger Peter van Inwagen Manuel Vargas John Venn Kadri Vihvelin Voltaire G.H. von Wright David Foster Wallace R. Jay Wallace W.G.Ward Ted Warfield Roy Weatherford C.F. von Weizsäcker William Whewell Alfred North Whitehead David Widerker David Wiggins Bernard Williams Timothy Williamson Ludwig Wittgenstein Susan Wolf Xenophon Scientists David Albert Philip W. Anderson Michael Arbib Bobby Azarian Walter Baade Bernard Baars Jeffrey Bada Leslie Ballentine Marcello Barbieri Jacob Barandes Julian Barbour Horace Barlow Gregory Bateson Jakob Bekenstein John S. Bell Mara Beller Charles Bennett Ludwig von Bertalanffy Susan Blackmore Margaret Boden David Bohm Niels Bohr Ludwig Boltzmann John Tyler Bonner Emile Borel Max Born Satyendra Nath Bose Walther Bothe Jean Bricmont Hans Briegel Leon Brillouin Daniel Brooks Stephen Brush Henry Thomas Buckle S. H. Burbury Melvin Calvin William Calvin Donald Campbell John O. Campbell Sadi Carnot Sean B. Carroll Anthony Cashmore Eric Chaisson Gregory Chaitin Jean-Pierre Changeux Rudolf Clausius Arthur Holly Compton John Conway Simon Conway-Morris Peter Corning George Cowan Jerry Coyne John Cramer Francis Crick E. P. Culverwell Antonio Damasio Olivier Darrigol Charles Darwin Paul Davies Richard Dawkins Terrence Deacon Lüder Deecke Richard Dedekind Louis de Broglie Stanislas Dehaene Max Delbrück Abraham de Moivre David Depew Bernard d'Espagnat Paul Dirac Theodosius Dobzhansky Hans Driesch John Dupré John Eccles Arthur Stanley Eddington Gerald Edelman Paul Ehrenfest Manfred Eigen Albert Einstein George F. R. Ellis Walter Elsasser Hugh Everett, III Franz Exner Richard Feynman R. A. Fisher David Foster Joseph Fourier George Fox Philipp Frank Steven Frautschi Edward Fredkin Augustin-Jean Fresnel Karl Friston Benjamin Gal-Or Howard Gardner Lila Gatlin Michael Gazzaniga Nicholas Georgescu-Roegen GianCarlo Ghirardi J. Willard Gibbs James J. Gibson Nicolas Gisin Paul Glimcher Thomas Gold A. O. Gomes Brian Goodwin Julian Gough Joshua Greene Dirk ter Haar Jacques Hadamard Mark Hadley Ernst Haeckel Patrick Haggard J. B. S. Haldane Stuart Hameroff Augustin Hamon Sam Harris Ralph Hartley Hyman Hartman Jeff Hawkins John-Dylan Haynes Donald Hebb Martin Heisenberg Werner Heisenberg Hermann von Helmholtz Grete Hermann John Herschel Francis Heylighen Basil Hiley Art Hobson Jesper Hoffmeyer John Holland Don Howard John H. Jackson Ray Jackendoff Roman Jakobson E. T. Jaynes William Stanley Jevons Pascual Jordan Eric Kandel Ruth E. Kastner Stuart Kauffman Martin J. Klein William R. Klemm Christof Koch Simon Kochen Hans Kornhuber Stephen Kosslyn Daniel Koshland Ladislav Kovàč Leopold Kronecker Bernd-Olaf Küppers Rolf Landauer Alfred Landé Pierre-Simon Laplace Karl Lashley David Layzer Joseph LeDoux Gerald Lettvin Michael Levin Gilbert Lewis Benjamin Libet David Lindley Seth Lloyd Werner Loewenstein Hendrik Lorentz Josef Loschmidt Alfred Lotka Ernst Mach Donald MacKay Henry Margenau Lynn Margulis Owen Maroney David Marr Humberto Maturana James Clerk Maxwell John Maynard Smith Ernst Mayr John McCarthy Barbara McClintock Warren McCulloch N. David Mermin George Miller Stanley Miller Ulrich Mohrhoff Jacques Monod Vernon Mountcastle Gerd B. Müller Emmy Noether Denis Noble Donald Norman Travis Norsen Howard T. Odum Alexander Oparin Abraham Pais Howard Pattee Wolfgang Pauli Massimo Pauri Wilder Penfield Roger Penrose Massimo Pigliucci Steven Pinker Colin Pittendrigh Walter Pitts Max Planck Susan Pockett Henri Poincaré Michael Polanyi Daniel Pollen Ilya Prigogine Hans Primas Giulio Prisco Zenon Pylyshyn Henry Quastler Adolphe Quételet Pasco Rakic Nicolas Rashevsky Lord Rayleigh Frederick Reif Jürgen Renn Giacomo Rizzolati A.A. Roback Emil Roduner Juan Roederer Robert Rosen Frank Rosenblatt Jerome Rothstein David Ruelle David Rumelhart Michael Ruse Stanley Salthe Robert Sapolsky Tilman Sauer Ferdinand de Saussure Jürgen Schmidhuber Erwin Schrödinger Aaron Schurger Sebastian Seung Thomas Sebeok Franco Selleri Claude Shannon James A. Shapiro Charles Sherrington Abner Shimony Herbert Simon Dean Keith Simonton Edmund Sinnott B. F. Skinner Lee Smolin Ray Solomonoff Herbert Spencer Roger Sperry John Stachel Kenneth Stanley Henry Stapp Ian Stewart Tom Stonier Antoine Suarez Leonard Susskind Leo Szilard Max Tegmark Teilhard de Chardin Libb Thims William Thomson (Kelvin) Richard Tolman Giulio Tononi Peter Tse Alan Turing Robert Ulanowicz C. S. Unnikrishnan Nico van Kampen Francisco Varela Vlatko Vedral Vladimir Vernadsky Clément Vidal Mikhail Volkenstein Heinz von Foerster Richard von Mises John von Neumann Jakob von Uexküll C. H. Waddington Sara Imari Walker James D. Watson John B. Watson Daniel Wegner Steven Weinberg August Weismann Paul A. Weiss Herman Weyl John Wheeler Jeffrey Wicken Wilhelm Wien Norbert Wiener Eugene Wigner E. O. Wiley E. O. Wilson Günther Witzany Carl Woese Stephen Wolfram H. Dieter Zeh Semir Zeki Ernst Zermelo Wojciech Zurek Konrad Zuse Fritz Zwicky Presentations ABCD Harvard (ppt) Biosemiotics Free Will Mental Causation James Symposium CCS25 Talk Evo Devo September 12 Evo Devo October 2 Evo Devo Goodness Evo Devo Davies Nov12 |
How a "Hidden" Constant of the Motion Can Explain Einstein's "Spooky Action at a Distance"
See how a Common Cause, Constant of the Motion, and Spherical Symmetry are needed to produce the perfectly correlated (and random) outcomes of two-particle Bell experiments.
Abstract
Whether a calcium cascade or a spontaneous parametric down-conversion, the spins of two entangled particles are projected into a singlet state whose wave function is spherically symmetric with total spin zero. As the particles travel to the distant measurement devices the total spin zero is conserved in the absence of environmental interactions and is a constant of the motion. As long as the two measurement devices are set at the (pre-agreed upon) same angle, they will have planar symmetry. Their measurement angle can then be arbitrary and the interactions will still produce perfectly correlated results. The argument by Bohm1 and Mermin2 that particles spins would need to be defined in all three x, y, z directions (which of course is impossible) is not correct. The requirement is that there be no preferred direction at entanglement and a single arbitrary direction chosen for the two measurements. Preface
Albert Einstein in 1905 had concerns that lasted for decades about what he thought were instantaneous interactions or "influences" between quantum particles that he thought had been long "separated." In 1947 he called it "spooky action at a distance." Such events are today called "nonlocal" or "entangled."
Today hundreds of experiments with two entangled particles confirm that measurements made at arbitrarily large separations show the two particles' properties are perfectly correlated, even though the individual particle properties are found to be random, an unusual combination of determined and indeterministic.
Widely separated events, happening simultaneously in a frame of reference including the entanglement preparation at the center between the particles, can give the false appearance of one event influencing the other at speeds much greater than the velocity of light.
Despite Einstein's great physical insight, and despite his deep understanding of conservation principles and mathematical and geometrical symmetries, he may have introduced a false asymmetry into a symmetric situation.
In the 1935 Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen paper, the properties measured were momentum and position, which are continuous variables. Since David Bohm in 1952, the entangled properties studied are spin angular momentum, which have discrete values much easier to measure.
Bohm proposed "hidden variables" might be found traveling along "locally" with the particles to explain their perfect correlations. No working physical model for such hidden variables has been proposed.
Entanglement experiments are usually described with two widely separated experiments at points A and B with experimenters, Alice and Bob, typically located symmetrically about the center C where two particles become entangled.
| ψAB > = 1/√2) | A+ B- > - 1/√2) | A- B+ >
We can read the first two-particle state | A+ B- > as particle A being plus (or spin-up) and particle B being minus (or spin-down). The particles are in "opposite" states.
The second two-particle state | A- B+ > reverses the signs of the two particles.
We can also simplify the notation for later discussions as
| ψ > = (1/√2) | + - > - (1/√2) | - + >
Dirac explains the coefficients 1/√2 multiplying each two-particle state as a "probability amplitude" (which is often a complex number). The absolute square of a coefficient gives us the probability of finding the particles in that state. Squaring 1/√2 gives us 1/2 so the wave function tells us the particles will be found half the time in the state | + - > or "up-down" and the other half in | - + > or "down-up."
This sounds simple enough, but the wave function predicts that strange combination of determined and indeterministic outcomes we see in all the entanglement experiments.
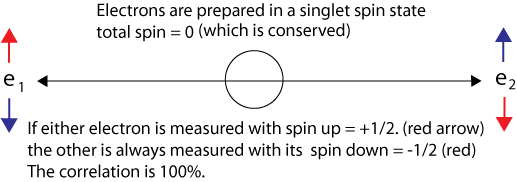
When we consider an individual particle its outcomes are random, either up or down, + or -. But when we look at the joint outcomes of two particles they are perfectly correlated, always one up and the other down, conserving the total spin zero, which is our "constant of the motion."
Bell's Theorem and a closer look at the experiment outcomes
Between Alice and Bob is an apparatus C that prepares entangled particles and ejects them in opposite directions heading towards the measurement devices at A and B, which can be arranged at different angles. As Alice and Bob look in the direction of the initial entanglement, they can agree on angles called "up" and "down," as well as "left" and "right" which are perpendicular to the "up-down" directions.
Each of the measuring devices can be freely rotated from the "up" direction, which we can call zero degrees, turning it clockwise around 90 degrees to the "right" direction," on to 180 degrees in the "down" direction, then to 270 degrees in the "left" direction, and finally ninety more degrees points the device back to the "up " direction.
John Bell's famous theorem made predictions about the results Alice and Bob should measure at various angle settings. But what do experimental results show? We can describe the results as "up" or "down," or plus or minus, or with digital bit sequences 1 or 0.
Alice's measurement sequences appear to her to be completely random, like this, with approximately equal numbers of 1's and 0's, approaching equality for longer bit sequences.
00010011011110101100011011000001
And Bob's sequence looks to him to be equally random, with 1's and 0's approaching 50/50.
11101100100001010011100100111110
But amazingly, should Alice send her bit sequence to Bob for comparison, he discovers that when he lines the bit strings up with one another, they are perfectly anti-correlated. Where Alice measured a 1, Bob measures 0, and vice versa. How can this be?
00010011011110101100011011000001
[Note that these random but perfectly correlated bit sequences are perfect for use as one-time pads for encrypting coded messages. And the sequences have not been "communicated" or "distributed" over an ordinary communication channel. They have been created independently and locally at Alice and Bob in a secure way that is invulnerable to eavesdroppers, solving the problem of quantum key distribution (QKD).]
Although he initially objected, Einstein came to accept that quantum mechanics predicts a random, uncertain outcome for the measurement of an individual particle, following Werner Heisenberg's "uncertainty principle," or Paul Dirac's "projection postulate," which says the particle is statistically found in a state proportional to the probability for each possible state.
But if the two particle states are individually random (indeterminism), how can together they always are found jointly correlated (determinism)?
Many scientists, starting with David Bohm in 1952, think there are "local hidden variables," traveling along with each particle, carrying "instructions" that tell each particle how to correlate with the other.
John Bell's test experiments were said to distinguish between "local" and "nonlocal" hidden variables. Bell concluded that if hidden variables do exist, they must be "nonlocal." But no reasonable physical explanation for how such variables work, local or nonlocal, has been given.
11101100100001010011100100111110
How a "hidden" constant of the motion produces the exact results predicted by the two-particle wave function ψAB.
Our proposed explanation for events that are independently random but are perfectly correlated jointly is a "condition" or "constraint" that travels along with the particles from their initial entanglement, so it is a phenomenon local to each particle, coming from a point in space that is in the past light cone of both particles.
The "condition" is a consequence of a deep principle that is fundamental to both quantum physics and classical physics. It's the law of conservation of certain quantities, like mass, charge, linear momentum, and angular momentum. As Emmy Noether taught us, conservation laws are the consequence of geometrical symmetries.
So our "condition" depends on the spherical symmetry of the wave function for two particles in a so-called "singlet" state. The two 1s electrons in the filled shell of the helium atom are in such a spherically symmetric state. These molecular orbitals are spheres with the electrons equally likely to appear at any point, though if both could be found they would most likely be located opposite one another because of their mutual repulsion. The total spin angular momentum is zero. Electron spins are exactly opposite at all times.
A similar situation is the 1Σg singlet state of the two atoms in a hydrogen molecule. The two hydrogen atoms in the hydrogen molecule ground state 1Σg+ are rotationally symmetric about the molecule axis. David Bohm's hidden variable experiment in 1952 started with a hydrogen molecule that was dissociating into two hydrogen atoms with total spin zero.
As the hydrogen atoms "separate," the quasi-molecular wave function remains rotationally symmetric around the molecular axis. The total spin angular momentum remains zero at all times, unless the atoms are disturbed by the environment or a measurement is made.
This conservation of total spin angular momentum is equal to zero at all times, up to and including the measurements made by Alice and Bob, but if, and only if, 1) nothing external has disturbed their state since entanglement, and 2) their two measurements are made at exactly the same measurement angles, preserving the overall symmetry. Alice and Bob must agree before they experiment to the free choice of one angle in which to measure.
They must also measure at the same time (assuming the initial entanglement is centered between their measurement devices), to ensure they are measuring the correct pair of particles.
Should Alice and Bob measure at different angles, say angles separated by angle θ, they will lose the perfect correlations. Correlations will decline proportional to the square of the cosine of that angle difference, cos2θ. If they measure at right angles to one another, there will be no correlations, since the cosine of 90 degrees is zero.
For reasons that are hard to discern, John Bell's theorem predicts this falloff in correlations would have a different angular dependence for quantum physics (curved) than for local hidden variables (linear). We discuss his results below and on Bell's web page.
Perhaps "hidden constant" is too clever, although it travels along with the particles just as David Bohm's hidden variables or David Mermin's "instruction sets" do.
A more modest name is simply a common cause, coming from that event in the shared light cone of the two particles, when they were initially entangled. But there is a distinction between a physical cause and a conservation principle that needs explaining.
A conserved physical quantity that does not change as particles move around is called a "constant of the motion." Since we believe it can fulfill the function that David Bohm and John Bell thought their hidden variables could do, we have chosen to call the conserved total spin angular momentum zero a "hidden constant of the motion."
There has not been any proposal as to how hidden variables might causally act on the two particles to produce that "action at a distance" that produces the particles with opposite spins.
Our proposal starts with two local causal interactions at initial entanglement in the causal center C followed by the conserved constant of the motion as the particles travel to A and B. It ends with two local causal interactions which create one bit of information in each of the measurements at A and B. No information travels between A and B.
Our "hidden constant" does not involve any faster-than-light "spooky" actions-at-a-distance to produce the opposite spins. As long as there is no asymmetric actions on the separating particles that would change their conserved states of opposite spin, the "hidden constant" gives us the perfect correlation that is experimentally observed.
Between 1905 and 1927 Einstein puzzled over "nonlocal," apparently faster-than light, effects between a light quantum (a photon) and its light wave, between a material particle (an electron) and its deBroglie matter wave, then between the abstract Schrödinger "wave function" ψ and a single particle. This is the modern problem of wave-particle duality and the so-called "collapse" of the wave function..
It was not until 1933, in a conversation with Leon Rosenfeld, that Einstein first considered what he thought were "nonlocal" effects between two particles that had collided and separated with equal and opposite velocities. Measuring the position of one would tell us the position of the other, he said. This is true because the two particles have travelled equal distances from the collision, but not because they are still interacting, as Einstein feared. It is simply the conservation of total linear momentum they puts them at the same distance from the collision. We wish it had been called "knowledge at a distance."
In 1935, Einstein and his colleagues Boris Podolsky and Nathan Rosen suggested in their EPR paradox paper1 that quantum mechanics is not "complete" and that additional parameters might be needed to complete it. Their argument suggested simultaneous measurements of position and momentum that might violate Heisenberg's uncertainty principle. In later years, Einstein distanced himself from this attack on uncertainty and said his concern was ony "nonlocal" behavior.
What Einstein twelve years later called "spooky actions at a distance" conflicted with his view of physical reality as limiting interactions to "local" forces or fields, with any interactions proceeding at the speed of light or less.
But Erwin Schrödinger, in his reply to EPR, promptly told Einstein that the "entangled" two-particle wave function ψ12 cannot be "separated" into the product of independent single-particle wave functions ψ1 and ψ2 without a "disturbance" or a "measurement."
In 1952 David Bohm reformulated the two material particles of EPR as two atoms in a hydrogen molecule in the singlet 1Σg state separating as the molecule dissociates into two atoms in 1s states (with spins at all time in opposite directions to conserve spin angular momentum equal to zero)
. Bohm replace the continuous properties of position and momentum of EPR with the discrete ℏ spins of the two atoms.
Until the two-particle wave function ψ12 has decohered and the particles have been disentangled by a disturbance or a measurement, Schrödinger said the particles are in a linear combination or "superposition" of states, according to the modern transformational theory of quantum mechanics formulated by Paul Dirac, which combined the 1925 matrix mechanics of Werner Heisenberg and the 1926 wave mechanics of Erwin Schrödinger.
ψ12 = 1/√2(ψ+1 ψ-2 - ψ-1 ψ+2) (1).
Measurements will find particles randomly in either the ψ+1 ψ-2 state or the ψ-1 ψ+2 state.
Quantum mechanics says that the resulting states of the two particles "did not exist" before the measurement. Dirac says the particles are "projected" into their states probabilistically, statistically, or indeterministically. Heisenberg said the states are "created" by the measurement.
We will demonstrate below that the final measured spin states of the individual particles could not have been determined at their original entanglement, but that the spherical symmetry of the two-particle wave function was determined at that time. And as long as the wave function is not decohered by the environment as it expands and the particles "separate," and as long as the measurements are made at A and B at the same measurement angle to preserve the spherical symmetry, the spin measurements will be opposite and perfectly correlated.
Each particle will be found 50/50 randomly in a + state (a spin-up state) or in a - state (a spin-down state).
But counterintuitively, the fact that two spins are always found opposite one another (either + - or - +, either up-down or down-up) is not random, indeterministic, or uncertain. It is determined because the total spin is conserved to be zero from the time of the particles initial entanglement. The total spin angular momentum of the two particles is zero from the initial entanglement up to and after the measurement, a "constant of the motion," unless the measurements are made asymmetrically, destroying the spherical symmetry of the original two-particle state.
Even in this case the fundamental conservation law for total spin angular momentum is not violated. The asymmetric measurements have acted on the particles differently, and their equal and opposite reactions have been different. But momentum exchange between each particle and its measuring apparatus will exactly balance and conserve total angular momentum of particles and apparatus, as it must.
So total spin angular momentum zero will be found conserved if, and only if, the spin measurements are made in exactly the same direction (detector angle or polarization angle), preserving the (now planar) symmetry.
Measurements whose detector or polarization angles differ by angle θ would introduce an asymmetry that reduces the correlations between distant measurements. This falloff in correlations as the angle of measurements between A and B increases is at the heart of John Bell's famous "inequality" theorem, which Bell said could distinguish between local and nonlocal phenomena.
If measurements are made at angles different by θ the total spin of the particles will no longer be zero and the correlations will no longer be perfect. Quantum mechanics predicts that the correlations will be reduced by cos2θ, the square of the cosine of the difference in measurement direction or in polarization angles. This has long been known as the "law of Malus" for crossed polarizers.
In 1952 David Bohm,2 inspired by Einstein's hope for "completeness," proposed "hidden variables" that could travel along with the particles (thus be considered "local") from their initial entanglement to ensure their perfect correlation of properties in any later measurements.
In 1964 John Bell4 proposed a theorem and experimental tests that could confirm (or deny) these "local hidden variables." Critical experimental tests made between 1972 (Stuart Freedman and John Clauser5) and 1982 (Alain Aspect6) denied the existence of local hidden variables by violating the Bell "inequalities."
The Bell-test experiments confirmed the existence of the mysterious "nonlocal" behavior and the failure of what Einstein called his "separability principle (Trennungsprinzip)."
Entanglement is thus a physically "real," if "weird," phenomenon which became the basis for the so-called "second quantum revolution," leading to quantum cryptography, quantum teleportation, and quantum computing.
The 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Clauser, Aspect, and Anton Zeilinger for their experiments confirming entanglement. The Nobel Prize committee mistakenly said that these experiments mean that "quantum mechanics cannot be replaced by a theory that uses hidden variables." But the work of John Bell and the dozens of experimenters who confirmed his predictions only denied the existence of "local" hidden variables. We will show that their work confirms the appearance of nonlocality, but not the actual reality of "faster-than light" nonlocal behavior, which is simply impossible according to Einstein's principle of special relativity.
We propose the conservation of spin angular momentum zero in the original spherically symmetric singlet state is a "constant of the motion," necessarily true at all times as long as the particles are not disturbed by the environment. This "constant of the motion" determines that the particle spins will jointly be found opposite one another at the distant points A and B, despite the randomness for each of the individual particles' spin direction when measured. Particle measurements are independently random but joint measurements are determined to be opposite and perfectly correlated.
There is no "instantaneous" interaction between the distant particles, or any "influence" of one particle on the other, at the time of measurement, rather there was a pair of interdependent actions that were "simultaneous" in the past in the frame of reference and at the time of the original entangling state preparation. These initial entangling actions can be considered "local," happening inside the atomic or molecular wave functions of the particles.
The "constant of the motion" can be "understood" as a "common cause" coming from the shared past light cone ot the particles. This explains the perfect correlations found in Bell-test experiments as "caused" by the "condition" on total spin imposed on the particles at their creation. It is not a mechanical model of instantaneous particle "interactions" pushing and pulling, which would violate relativity and is no more realistic than Niels Bohr's semi-classical model of electron "orbits" in atoms.
The perfectly correlated opposite spins are also not the specific spin directions created at initial entanglement. Such specific spin directions would only accidentally align with the experimenters' freely chosen directions (which preserve a planar symmetry) at A and B. The constant of the motion is the total spin zero state, symmetric in all directions, which means as long as the same measurement direction is freely chosen at A and B (by prior agreement), the particles will be found in perfectly correlated opposite states!
Exactly how the bit strings of data at A and at B are indeterministically random, even as the combined A and B results appear to be deterministically correlated, is only explained by the "collapse" of the "superposition" of states above. Whether spin is up or down for each particle "did not exist" before the measurements, as the Copenhagen interpretation maintains. The particles spins are individually random but jointly determined.
Let's look more closely at the extraordinary mathematical predictions of quantum mechanics. Equation 1 can be written more simply with Dirac's <bra| and |ket> notation as
ψ12 = 1/√2 (| + > | - > +/- | - > | + >) (2).
[The plus sign in the middle applies to photons and other bosons which are symmetric under interchange of identical particles and the minus sign applies to electrons and other fermions that are anti-symmetric (they change sign) when interchanged.]
We square the coefficient 1/√2 to predict that 1/2 of the measurement outcomes will be | + > | - > and the other half will be | - > | + >.
The individual particles are randomly | + > or | - >, but the total spin is determined to be always zero, always opposite spins, whether | + > | - > or | - > | + >.
Quantum mechanics does not predict outcomes like | + > | + > or | - > | - >. They are never seen in "perfect" experiments, although they may be found in practice because of system noise or other experimental errors. For example, the measurement directions might not be exactly parallel.
Should outcomes like | + > | + > or | - > | - > be observed, they would violate a conservation law, and conservation laws are the most fundamental laws of both quantum physics and classical physics.
The History of Single-particle Nonlocality and Two-particle Entanglement
We argue that the problems of nonlocality and entanglement began with Einstein's photoelectric effect in 1905 and cannot be fully understood by starting thirty years later with the famous Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen paper, as is done by most commentators on entanglement.

Introduction
As Louisa Gilder has written,11 we live in "The Age of Entanglement." Entanglement is the basis of powerful new technologies like quantum cryptography, quantum teleportation, and quantum computing, which Lars Jaeger20 and others call "The Second Quantum Revolution."
Although these technologies are new, the "weirdness" of entanglement is not something new.
We will show that it is partly based on what Richard Feynman called the "central mystery of quantum mechanics," the "general mystery," and the "only mystery" in quantum mechanics, which led Feynman to famously say "nobody understands quantum mechanics."
Feynman's central mystery is the two-slit experiment, the problem of a particle (or its "wave") appearing to go through two slits and "interfering" with itself to produce characteristic diffraction patterns on a distant screen.
Feynman told us we cannot hope to "understand" what is going on in quantum mechanics in terms of processes we have learned from our everyday experiences of classical mechanics. But he said he could describe what is happening for us in the two-slit experiment.
In a similar vein, Paul Dirac argued that the non-intuitive concepts of quantum mechanics, though impossible to understand in terms of continuous classical concepts, could be mastered through long familiarity with them. He wrote...
The new theories, if one looks apart from their mathematical setting, are built up from physical concepts which cannot be explained in terms of things previously known to the student, which cannot even be explained adequately in words at all. Like the fundamental concepts (e.g. proximity, identity) which every one must learn on his arrival into the world, the newer concepts of physics can be mastered only by long familiarity with their properties and uses.By contrast with Feynman and Dirac, Niels Bohr and Werner Heisenberg, in their Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics, said that the results of quantum measurements must be expressible in classical concepts because it is the language that humans can understand. Sadly, the Copenhagen Interpretation has led to a great deal of confusion. Following Feynman's and Dirac's suggestion of simply making you familiar with quantum phenomena, we try to describe, with words, diagrams, and a minimum of equations, several essential quantum phenomena... 1) Feynman's "only mystery," the two-slit experiment. 2) Wave-particle duality. 3) Erwin Schrödinger's "wave function" ψ that describes the wave as well as 4) | ψ |2, the absolute square of the wave function, which first Einstein and later Max Born interpreted as giving us the probabilities of finding the particle at one of its possible locations (which is now the "standard" interpretation of quantum mechanics). Einstein said this about the wave function...|ψ|2 expresses the probability that there exists at the point considered a particular particle of the cloud, for example at a given point on the screen.5) the so-called "collapse" of the wave function which describes the random appearance of a particle at a certain location and with random properties when measured. This indeterminism and probabilistic or statistical aspect of quantum mechanics greatly bothered Einstein, who hoped such properties existed before their measurement. But we are not there yet. It takes two particles to be entangled. The two-slit experiment involves a single particle and its wave (function) going through two slits. Entanglement involves two particles measured when their two-particle wave function ψ12 has spread out in all directions at the speed of light, so that when measured they are most likely to be found a great distance apart, but not yet physically "separated!" Schrödinger said that a wave function describing two entangled particles must be in what Paul Dirac called a superposition We must also explain the deep meaning of superposition of states, which is frequently and mistakenly described as "being in two states (or places) at the same time." Schrödinger poked fun at Dirac's superposition and its probabilities (which Schrödinger and Einstein did not like) with his famous cat that was dead and alive at the same time. Although he was skeptical about superpositions of states in the late 1920's, Schrödinger wrote Einstein in 1935 that the two-particle wave function would keep the particles entangled and "not separated" until a measurement would produce either | + - > or | - + > which he said could be rewritten as the product of two single-particle states, either | + > | - > or | - > | + >, both of which will have decohered and disentangled and become independent of one another. Note that the random appearance of either | + - > or | - + > means that the bit string of values for each particle is a random sequence, but the two particles are always in opposite states, never violating the conservation of total spin zero. Beyond superposition, we must also say something about 7) Werner Heisenberg's 1927 uncertainty principle. Heisenberg said his principle introduced indeterminism and acausality into quantum mechanics, but Einstein had shown in 1916 that the emission of light quanta involves ontological chance. And the collapse of the two-particle superposition of states into a product of single-particle states is ontologically random. Heisenberg said the product of uncertainty in the position ∆x multiplied by the uncertainty in momentum ∆p is equal to Planck's constant ℏ. The more certain we are of position, the less certain we are of momentum. He wrote
∆p∆x = ℏ
We may think about Heisenberg's uncertain position as the dimension in position space where Schrödinger's wave function is non-zero, and the uncertain momentum as the dimension of momentum space where Schrödinger's wave function is non-zero, so the dimension of so-called phase space (position x momentum) as ℏ, and the minimum phase-space volume that can be occupied by two spin 1/2 particles is ℏ3, the volume of the first electron shell in atoms.
We should note that Heisenberg's uncertainty in 1927 was already implicit in Schrödinger's wave function, which Einstein had long interpreted as the probability of finding particles, though he gave full credit to Max Born for the idea, which became known as Born's Rule.
And Einstein's interpretation of quantum theory as probabilistic and quantum experiments as statistical goes back to his 1916 discovery of ontological chance in the emission and absorption of light quanta by atoms. But Einstein called this fundamental randomness a "weakness in the theory" and spent the rest of his life exploring the possibility of a deterministic theory underlying indeterministic quantum mechanics, making him the foremost critic of quantum mechanics, though all his life he was more concerned about nonlocal effects between particles and between particles and their waves.
Finally, we need to describe principles that are fundamental to both quantum mechanics and classical mechanics.
8) Conservation Laws
The principle is the conservation of some fundamental properties of physics, like mass, energy, and momentum. According to Emmy Noether these conserved properties emerge from certain symmetries in space.
Our proposed explanation of entanglement as resulting from the spherical symmetry of the two-particle wave function and the conservation of spin angular momentum as a "constant of the motion" will therefore not be simple, but we hope to make it as clear as possible.
Chapters (of book) Parts (of this web page)
In part 1 we show that Einstein's concerns about nonlocality can be glimpsed as early as his "miracle year" of 1905 in his photoelectric paper. See Photoelectric Effect
In 1909 Einstein described how a high-energy electron could eject a high energy light wave from a metal plate and radiate in all directions. A small part of the wave could hit a second plate and eject an electron with energy almost equal to the original electron, but in a random direction. See Wave-Particle
Einstein drew an illustration of the nonlocality problem on a blackboard at the Solvay conference in 1927. See Einstein at Solvay
He challenged Leon Rosenfeld to explain two-particle nonlocality in 1933. See Rosenfeld Lecture
This was just two years before Einstein's colleagues Boris Podolsky and Nathan Rosen published the famous "EPR Paradox," the most cited scientific paper in history. In a letter to Max Born in 1947 Einstein described it as "spooky action at a distance." And in his 1949 "Autobiography" he said the measurement of one particle "telepathically changes the real situation" of the second particle.
In part 2, we discuss the famous EPR paradox of 1935 and Einstein's fears about possible violations of special relativity.
In part 3, we see that Erwin Schrödinger replied to the EPR paper by saying that his two-particle wave function ψ12 would keep the particles "entangled" until a measurement projects them (i.e., collapses the two-particle wave function) into a product of two single-particle wave functions ψ1 and ψ2, only after which the particles would be "disentangled" (decohered) and could then actually "separate," as Einstein insisted.
In part 4, we see how David Bohm in 1952 replaced Einstein's continuous variables of position and momentum with the discrete variables of electron spins, making future experimental measurements practically possible. Bohm also revived Louis de Broglie's "pilot-wave" theory which offered a way of imagining hidden variables that are "guiding" the particles and suggested a new (Bohmian) mechanics that could restore determinism, eliminating quantum indeterminism.
We can now show that Dirac's principle of superposition of states <1/√2) | 1+2-> + 1/√2) | 1-2+>, which for Schrödinger led to his famous "cat both dead and alive," can explain both the 50/50 randomness of outcomes and the perfect correlations (or anti-correlations) of spin measurements.
In part 5, we explain why the perfectly correlated electron spins could not have been determined at the time of the initial entanglement preparation, with one spin up and the other down in a particular direction. Some physicists said that the electron spins would have to have been defined in all three dimensions - x-spin, y-spin, and z-spin. But this is impossible. In 1957 Bohm and Aharonov showed that that electron spins could be defined in at most a single direction, and this would not be the random freely chosen direction of the experimenters...
In quantum theory, a difficulty arises, in the interpretation of the above experiment, because only one component of the spin of each particle can have a definite value at a given time. Thus, if the x component is definite, then the y and z components are indeterminate and we may regard them more or less as in a kind of random fluctuation.But having opposite spins in even a single preferred direction would not explain the experimental data! Had there been a single preferred direction (or angle) for electron spins in the initial entanglement preparation, there is essentially zero chance that Alice and Bob could observe in precisely that (unknown) direction or angle. And observations at angle θ to that initial preferred direction will produce decorrelated results + + and - - proportional to sin2θ. In part 6, we will show that no preferred direction exists in the initial entanglement preparation. The original entangled state with total spin angular momentum zero is rotationally and spherically symmetric, the same in all directions. The preferred direction of measurement or angle for Alice and Bob is introduced by them, agreed to before they measure! Total spin angular momentum is conserved as zero at all times from the initial entanglement to their measurements (assuming that no environmental interaction disturbs either particle). As long as Alice and Bob now measure in the same plane (same direction, same angle), a new planar symmetry replaces the spherical symmetry and defines the one component of electron spin that Bohm and Aharonov say is allowed. The conservation of total angular momentum zero continues. As long as Alice and Bob measure in the chosen plane (preserving the symmetry), they maintain that conservation of total spin angular momentum. The conserved total spin zero is a candidate for a "hidden constant of the motion." In part 7, we examine John Bell's theorem predicting how correlations between measurements made at differing angles could distinguish between local hidden variables and quantum mechanics. We show how the correlations would be reduced if Alice and Bob's measurement angles differ by θ degrees. And we will examine Bell's hypothesis about how the falloff of correlations with increasing angle θ is different for local hidden variables (straight line function of θ) and for quantum mechanics (curved cosθ function). In part 8, we comment on the origin of the flawed idea that something must be traveling from Alice to Bob. Assuming, for the moment, that the entangled particles do not have perfectly correlated opposing spins, what kind of interaction could Alice's measurement produce to bring Bob's spin angular momentum into agreement. Would it not first have to detect the amount of angular deviation? And then what kind of torque could it exert from far away to rotate the remote particle precisely into agreement? In part 9, we criticize the argument that perfectly opposed spins at the time of the Alice and Bob measurements (and in the arbitrary direction chosen by them) would require that the spins be defined in all three axial directions, which is impossible. When spins are defined in one direction, they are necessarily undefined in the other two directions. In part 10, we review the work of some physicists, starting with Einstein, who used conservation principles to explain some aspects of entanglement, but without them seeing exactly how conservation of momentum could produce the appearance of Einstein's "spooky action at a distance." In part 11, we discuss the relation between conservation principles and geometric symmetries. Einstein was normally quite aware of symmetries and he greatly favored theories based on "principles" over those that are "constructed" to fit experimental data. In part 12, we comment on the idea of "instruction sets" accompanying the particles as "hidden variables." We trace the origin of this idea to Schrödinger's suggestion that the particles seemed to know the answers to all possible questions that would be asked of them when measured. What process could prepare such information and what mechanism could read the information in the "instructions" and then change the electron spin of the distant particle as required? In part 13, we conclude with a summary of the "hidden constant" hypothesis.
Part 1 Einstein and Nonlocality, from 1905 to 1927
We show that Einstein's concerns about nonlocality can be glimpsed as early as his "miracle year" of 1905 in his light quantum/photoelectric effect paper. Einstein wrote...
How can energy spread continuously over a large volume and later be absorbed in its entirety, without contradicting
his principle of relativity? Einstein sees this here, but does not say so explicitly until 1927. The energy of a ponderable body cannot be subdivided into arbitrarily many or arbitrarily small parts, while the energy of a beam of light from a point source (according to the Maxwellian theory of light or, more generally, according to any wave theory) is continuously spread over an ever increasing volume. The wave theory of light, which operates with continuous spatial functions, has worked well in the representation of purely optical phenomena and will probably never be replaced by another theory. It should be kept in mind, however, that the optical observations refer to time averages rather than instantaneous values. In spite of the complete experimental confirmation of the theory as applied to diffraction, reflection, refraction, dispersion, etc., it is still conceivable that the theory of light which operates with continuous spatial functions may lead to contradictions with experience when it is applied to the phenomena of emission and transformation of light. It seems to me that the observations associated with blackbody radiation, fluorescence, the production of cathode rays by ultraviolet light, and other related phenomena connected with the emission or transformation of light are more readily understood if one assumes that the energy of light is discontinuously distributed in space.In 1909 Einstein described how a high-energy electron could eject a high energy light wave radiating in all directions, a small part of which could hit a plate and eject an electron with energy almost equal to the original electron. In this work, Einstein gave us the first clear picture of wave-particle duality. In a presentation at the Salzburg conference in September, 1909, Einstein argued that the interaction of radiation and matter involves elementary processes that are not "invertible," a deep insight into the irreversibility of natural processes. While incoming spherical waves of radiation are mathematically possible, they are not practically achievable. Nature appears to be asymmetric in time. He speculated that the continuous electromagnetic field might be made up of large numbers of light quanta - singular points in a field that superimpose collectively to create the wavelike behavior. Although he could not formulate a mathematical theory that does justice to both the continuous oscillatory waves and the discrete particle pictures, Einstein argued that they could be "fused" and made compatible. This was over a decade before Erwin Schrödinger's wave mechanics and Werner Heisenberg's quantum mechanics. And because gases behave statistically, he knows that the connection between the wave and particles may involve probabilistic behavior. When light was shown to exhibit interference and diffraction, it seemed almost certain that light should be considered a wave. The greatest advance in theoretical optics since the introduction of the oscillation theory was Maxwell's brilliant discovery that light can be understood as an electromagnetic process...One became used to treating electric and magnetic fields as fundamental concepts that did not require a mechanical interpretation. This path leads to the so-called relativity theory. I only wish to bring in one of its consequences, for it brings with it certain modifications of the fundamental ideas of physics. It turns out that the inertial mass of an object decreases by L / c2 when that object emits radiation of energy L...the inertial mass of an object is diminished by the emission of light.In 1927, Einstein drew an illustration of the nonlocality problem on a blackboard at the fifth Solvay Conference in Brussels, Belgium. Sadly, despite Einstein's two decades of pioneering work on the interaction of photons and electrons, his ideas and concerns were given little attention at this Solvay, even though the conference was dedicated to electrons and photons! The conference was dominated by papers on the new quantum theory delivered by Louis de Broglie, Niels Bohr, Max Born, and Werner Heisenberg. It is best known for Einstein's after-hours suggestions to Bohr and Heisenberg probing for faults in the uncertainty principle. Accounts of these events have been told largely by the victors (there are no holes in uncertainty) but Einstein has said they often missed or ignored his important point. That point was the nonlocal behavior of a spherical light wave as it collapses to get absorbed by a single electron. This was Einstein's only contribution mentioned in the published proceedings. Here are the notes on Einstein's original remarks at the conference and Bohr's brief and confused response. They contain much of Einstein's future 1935 EPR paper, except in 1927 only one particle is involved. Entanglement in EPR requires two identical particles. Notice how Einstein's diagram clearly shows his concerns of over two decades about reconciling a spherical wave (his example is now an electron) and its collapse to being measured at just one point where it appears as a particle. At this point in the history of quantum mechanics, wave-particle duality is seen as the debate between Schrödinger's wave mechanics and Heisenberg's particle mechanics. Bohr's reaction to Einstein's presentation has been preserved. He didn't understand a word! He disingenuously claims he does not know what quantum mechanics is. His response is vague and ends with his ideas on complementarity and the inability to describe a causal spacetime reality. Twenty-two years later, in his contribution to the Schilpp memorial volume on Einstein, Bohr had no better response to Einstein's 1927 concerns. But he does remember vividly and provides a picture of what Einstein drew on the blackboard. Here is Bohr's 1949 recollection of Einstein's 1927 presentation:
At the general discussion in Como, we all missed the presence of Einstein, but soon after, in October 1927, I had the opportunity to meet him in Brussels at the Fifth Physical Conference of the Solvay Institute, which was devoted to the theme "Electrons and Photons."Although Bohr seems to have missed Einstein's point completely, Werner Heisenberg at least came to explain the 1927 presentation well. In his 1930 lectures at the University of Chicago, Heisenberg presented a critique of both particle and wave pictures, including a new example of nonlocality that Einstein had apparently developed since 1927. It includes Einstein's concern about "action-at-a-distance" that might violate his principle of relativity, and Heisenberg anticipates the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen paradox. Heisenberg wrote: In relation to these considerations, one other idealized experiment (due to Einstein) may be considered. We imagine a photon which is represented by a wave packet built up out of Maxwell waves. It will thus have a certain spatial extension and also a certain range of frequency. By reflection at a semi-transparent mirror, it is possible to decompose it into two parts, a reflected and a transmitted packet. There is then a definite probability for finding the photon either in one part or in the other part of the divided wave packet. After a sufficient time the two parts will be separated by any distance desired; now if an experiment yields the result that the photon is, say, in the reflected part of the packet, then the probability of finding the photon in the other part of the packet immediately becomes zero. The experiment at the position of the reflected packet thus exerts a kind of action (reduction of the wave packet) at the distant point occupied by the transmitted packet, and one sees that this action is propagated with a velocity greater than that of light. However, it is also obvious that this kind of action can never be utilized for the transmission of signals so that it is not in conflict with the postulates of the theory of relativity.
Part 2 EPR, Entanglement, and Suspected Violations of Special Relativity
Just two years before his colleagues Boris Podolsky and Nathan Rosen published the famous "EPR Paradox," the most cited scientific paper in history, in 1933 Einstein challenged Leon Rosenfeld to explain two-particle nonlocality. You will see that EPR is a version of this challenge to Rosenfeld.
Shortly before Einstein left Germany to emigrate to America,
Einstein attended a lecture on quantum electrodynamics by Leon
Rosenfeld. Keep in mind that Rosenfeld was perhaps the most
dogged defender of the Copenhagen Interpretation. After the talk,
Einstein asked Rosenfeld,
“What do you think of this situation?” Suppose two particles are set in motion towards each other with the same, very large, momentum, and they interact with each other for a very short time when they pass at known positions. Consider now an observer who gets hold of one of the particles, far away from the region of interaction, and measures its momentum: then, from the conditions of the experiment, he will obviously be able to deduce the momentum of the other particle. If, however, he chooses to measure the position of the first particle, he will be able tell where the other particle is. We can diagram a simple case of Einstein’s question as follows after the particles have interacted and separate from the center. We use electrons instead of Einstein's generic particles, an anachronism introduced by David Bohm in 1952. 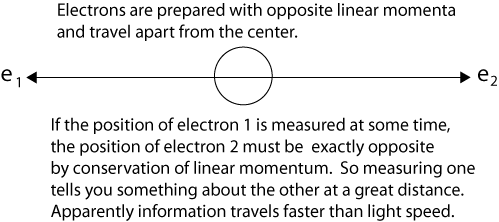
Recall that it was Einstein who discovered in 1924 the identical nature, indistinguishability, and interchangeability of some quantum particles. He found that identical particles are not independent, altering their quantum statistics.
After the particles interact at t1, quantum mechanics describes them with a single two-particle wave function that is not the product of independent single-particle wave functions. In the case of electrons, which are indistinguishable and interchangeable particles, it is not proper to say electron 1 goes this way and electron 2 that way. (Nevertheless, it is convenient to label the particles, as we do in the illustration.)
Einstein then asked Rosenfeld, “How can the final state of the second
particle be influenced by a measurement performed on the first
after all interaction has ceased between them?” This was the germ
of the EPR paradox, and ultimately the paradoxical problem of two-particle entanglement.
Why does Einstein question Rosenfeld and describe this as an “influence,” suggesting an “action-at-a-distance?”
One Einstein concern could see a paradox in the context of Rosenfeld’s Copenhagen
Interpretation, since the second particle is not itself measured and
yet we know something about its properties, whereas the Copenhagen Interpretation
says we cannot know any properties without an explicit measurement...
Einstein was clearly correct to tell Rosenfeld that at a later time t2, a measurement of one particle's position would instantly establish the position of the other particle - without measuring it. Einstein was implicitly using the conservation of linear momentum to calculate (and to know) the position of the second particle.
Another of Einstein's concerns may have been Werner Heisenberg's uncertainty principle. It suggests that knowing the exact position of the second particle is not possible. In any case, if the second particle were to be measured, it should be found in a range of positions Δx ≥ h/2πΔp. And this might contradict the conservation of linear momentum, as Nathan Rosen appears to have considered in the later EPR paper.
Two years later, reacting to EPR, Schrödinger described two such particles as becoming "entangled" (verschränkt) at their first interaction, so "nonlocal" phenomena are also known as "quantum entanglement."
Although conservation laws are rarely cited as the explanation, we argue that they are the physical reason that entangled particles always produce correlated results for all properties, linear momentum, angular momentum, and energy. If the results were not always correlated, the implied violation of a fundamental conservation law would cause a much bigger controversy than entanglement itself, as puzzling as that phenomenon is.
The hypothesis that the conservation principle gives us a "hidden constant" of the motion like the above linear momentum (perhaps three hidden constants to include angular momentum and energy?), can explain the above results.
In his 1935 EPR paper, Einstein cleverly introduced two particles instead of one, and in the same year Erwin Schrödinger would create a two-particle wave function that describes both particles. EPR described the particles as widely separated, one "here" and measurable "now" and the other distant and to be measured "later."
Here we must explain the asymmetry that Einstein mistakenly introduced into a perfectly symmetric situation, making entanglement such a mystery.
The two entangled particles must normally be measured at the same time (synchronously) to ensure that just one entangled pair is involved. This means the measuring devices are placed equidistant (symmetrically) from the central location of initial entanglement. Most accounts of entanglement say that Alice measures "first" and then must interact instantaneously with Bob's particle to align its spin with hers. This is a false asymmetry and an impossible interaction, as it is a violation of special relativity.
At creation, the wave function of the entangled pair is rotationally and spherically symmetric.
The measurement devices must be arranged symmetrically. in the same plane with the origin. If the measurements differ by an angle θ, the perfect correlations would be reduced by cos2θ.
The normal interactions between the separating particles (electromagnetic forces) do not exceed the speed of light and have the translational, rotational, and temporal invariance symmetries needed to conserve the total spin zero (as well as total linear momentum zero and total energy) created at initial entanglement.
All these symmetries are essential to creating perfectly correlated outcomes.
What could have led Einstein to see an asymmetry as an instantaneous action a distance. In his 1905 photoelectric study it was likely the view that the light wave was radiation energy spread out in space that had to collect itself into the photoelectron. In his 1909 wave-particle duality electron article, it was likely the view shared by Schrödinger that the wave was spread out electric charge. It lies behind the current concern with the collapse of the wave function.
The EPR paradox has been reframed since David Bohm in 1952 as two entangled electrons instead of generic particles conserving their total linear momentum zero. In this case, the particles are identical, indistinguishable, and interchangeable, with indeterminate positions according to the uncertainty principle.
We can diagram a simple case of indistinguishable electrons separating from their point of entanglement to be measured at a later time when they are far apart.
Note the anachronism of electrons as Einstein's generic particles. It was David Bohm in 1952 who proposed that Einstein's EPR problem use electrons. Today many if not most accounts of the EPR paradox describe it with electrons. Many mistakenly say that Einstein was describing electrons. 
| ψ12 > = (1/√2) | + - > - (1/√2) | - + >
The coefficients 1/√2, when squared, tell us the probabilities of either state being found is 1/2.
Dirac's superposition) can provide only the probabilities of finding the entangled system in either the | + - > state or the | - + > state. Quantum mechanics does not and cannot describe the paths or the spins of the individual particles as the wave function expands at the speed of light. Note that should measurements result in | + + > or | - - > state, that would violate the conservation of angular momentum. We call the conserved total spin zero a "hidden constant of the motion". It is the implicit reason why David Bohm, John Bell, and many others say that when one particle is measured spin-up, we instantly know the other must be spin-down.
Part 3 Erwin Schrödinger, Entanglement, and his Two-Particle Wave Function
Erwin Schrödinger replied to the EPR paper by telling Einstein that his two-particle wave function ψ12 would keep the particles coherently "entangled" until a measurement projects them into a product of single-particle wave functions ψ1 and ψ2. We show that the Schrödinger/Dirac superposition of states <1/√2) | 1+2- > - 1/√2) | 1-2+ > can explain both the 50/50 randomness of outcomes and the perfect correlations (or anti-correlations) of measurements, provided the spin angular momentum is conserved.
Schrödinger said that the entangled particles have jointly shared properties that cannot be changed independently, until after they have become disentangled, decoherent, and independent of one another. Though Schrödinger did not mention it, one of those properties is total linear momentum, key to the EPR paper.
But like Einstein's other reactions to quantum mechanics, he could not accept that particles he regarded as separated could change their properties simultaneously. Einstein did not explicitly recognize that the joint properties of the two particles would need to obey conservation laws, though he had implicitly used the conservation of linear momentum in 1933 and 1935, when he said the second particle position must be symmetrically placed.
Conservation laws are the consequence of extremely deep properties of nature that arise from simple considerations of symmetry. We regard these laws as "cosmological principles." Physical laws do not depend on the absolute place and time of experiments, nor their particular direction in space. Conservation of linear momentum depends on the translation invariance of physical systems, conservation of energy the independence of time, and conservation of angular momentum the invariance under rotations. Conservation laws are the consequence of symmetries, as explained by Emmy Noether.
Recall that the EPR experiment (Bohm version) starts with two electrons (or photons) prepared in an entangled state that is a mixture of pure two-particle states, each of which conserves the total angular momentum and, of course, conserves the linear momentum as in Einstein's original EPR example. This information about the linear and angular momenta is established by the initial state preparation (a measurement).
Quantum mechanics describes the probability amplitude wave function Ψ12 of the two-particle system as in a superposition of two-particle states. It is not a product of single-particle states, and there is no information about the identical indistinguishable electrons traveling along distinguishable paths. With slightly different notation, we can write equation (1) as
Ψ12 = 1/√2) | 1+2- > - 1/√2) | 1-2+ > (2)
The probability amplitude wave function Ψ12 travels away from the source (at the speed of light or less). Let's assume that at t0 observer A finds an electron (e1) with spin up.
At the time of this "first" measurement, by observer A or B, new information comes into existence telling us that the wave function Ψ12 has "collapsed" into the state | 1+2- > (or into | 1-2+ >). Just as in the two-slit experiment, probabilities have now become certainties, one possibility is now an actuality. If the first measurement finds a particular component of electron 1 spin is up, so the same spin component of entangled electron 2 must be down to conserve angular momentum. And conservation of linear momentum tells us that at t0 the second electron is equidistant from the source in the opposite direction. 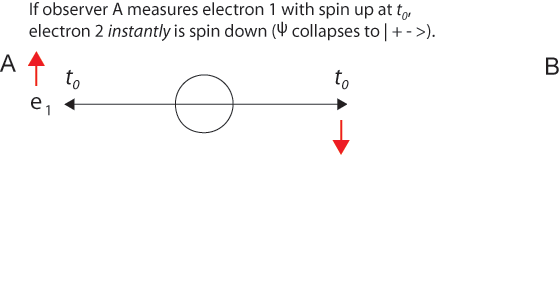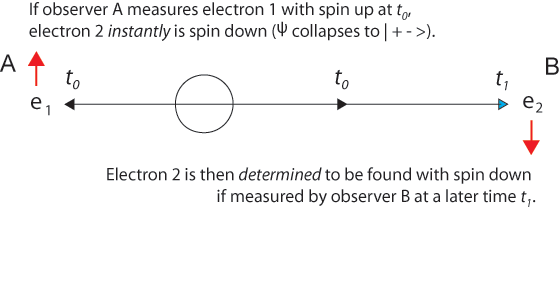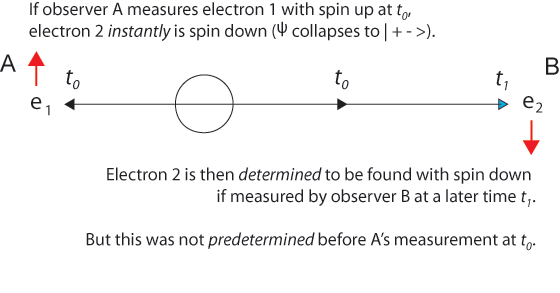
It was simply determined by her measurement.
Part 4 David Bohm, Atoms, Electron Spins, and Hidden Variables
As we saw in part 2, the first practical and workable experiments to test the EPR paradox were suggested in 1952 by David Bohm (though experiments were not realized for almost two decades). Instead of using continuous linear momenta in opposite directions, Bohm proposed using two atoms (or electrons) in discrete electronic spin states. The atoms are prepared in an initial molecular state of known total spin zero.
ψ12 = 1/√2(ψ1ψ2) - 1/√2(ψ2ψ1)
The coefficients 1/√2, when squared, tell us there is a 50-50 chance of finding the separated atoms in ψ1ψ2 or in ψ2ψ1. In either case the atomic spins are always found in opposite directions, when measurements are made in the same direction, preserving the symmetry, and conserving the total spin angular momentum as zero, the same as the original molecule.
It is this physical fact that let Bohm in 1951 write
Suppose that we have a molecule containing two atoms in a state in which the total spin is zero and that the spin of each atom is ℏ/2. Roughly speaking, this means that the spin of each atom points in a direction exactly opposite to that of the other, insofar as the spin may be said to have any definite direction at all. [Indeed, we can only say that the total spin zero of the two atoms means that their two-particle wave function ψ12 is spherically symmetric with no preferred direction - the singlet state.] Now suppose that the molecule is disintegrated by some process that does not change the total angular momentum. The two atoms will begin to separate and will soon cease to interact appreciably. [But Erwin Schrödinger tells us that they will not become independent and "cease to interact" until some measurement disentangles them, decohering their phases, and allowing their two-particle wave function to be replaced with the product of two single-particle wave functions ψ1ψ2 or ψ2ψ1.] Their combined spin angular momentum, however, remains equal to zero, because no torques have acted on the system... Suppose now that one measures the spin angular momentum ofany one of the particles, say No.1. Because of the existence of correlations we can immediately conclude that the angular momentum vector of the other particle (No.2) is equal and opposite to that on No.1. In this way, we can indirectly measure the angular momentum of particle No.2 by measuring the corresponding vector of particle No.1.Bohm and Yakir Aharonov said the equivalent in 1957 Then, because the total spin is still zero, it can immediately be concluded that the same component of the spin of the other particle (B) is opposite to that of A.Finally, in John Bell's first paper, he wrote in 1964 With the example advocated by Bohm and Aharonov, the EPR argument is the following. Consider a pair of spin one-half particles formed somehow in the singlet spin state and moving freely in opposite directions. Measurements can be made, say by Stern-Gerlach magnets, on selected components of the spins σ1 and σ2. If measurement of the component σ1 • a, where a is some unit vector, yields the value + 1 then, according to quantum mechanics, measurement of σ2 • a must yield the value — 1 and vice versa.Now why, we may ask, did not Bohm, or Bell, or modern commentators on Bell's theorem, consider the conservation of total spin angular momentum zero as a "common cause" explanation for the perfect measurement correlations? The conservation is true at all times for the "separating" particles (now known as a "quasi-molecule" because it is described with a molecular wave function and not the product of two atomic wave functions). Conservation will remain true as long as the forces involved in Stern-Gerlach spin measurements are symmetric, the two SG devices oriented in the same plane to preserve the symmetry. When the devices measure in planes at an angle to one another, the correlations fall off as the cosine squared of that angle (Malus's law). This "common cause" is just a shared/joint property of the two particles, true at all times, not just for measurements. It is not one particle's measurement acting (instantaneously at a distance) on the other particle. The constant total spin zero is thus a "constant of the motion." Since it achieves the goal of hypothetical "local hidden variables" traveling with the particles, we might call it a "hidden constant of the motion."
Part 5 Were the Spin Variables Created at the Initial Entanglement?
We comment on the flawed idea that something (hidden variables?) must be traveling between Alice and Bob. Assuming, for the moment, that the entangled electrons do not already have perfectly correlated opposing spins (which they will have if the electrons are conserving total spin angular momentum zero), 1) what kind of sensor would Alice need to measure the deviation between their electron spins and 2) what kind of interaction could Alice's measurement generate and send to Bob to bring his spin angular momentum into agreement? Alice must first detect the amount of Bob's angular deviation from her measurement angle. (Keep in mind that an electron spin measuring device, for example, a Stern-Gerlach device, would change the electron spin to be in the direction of the SG device. But Alice could not send an SG device to Bob, especially instantaneously!) Otherwise, what kind of torque could Alice exert on Bob's remote electron from far away to rotate it precisely into agreement? Any such two-part interaction, first signals about his orientation (pure information) from Bob to Alice and then mechanical forces back from Alice to Bob, applied to his electron in a distant space-like separation. Both violate the no-signaling theorem and the principle of relativity.
We explain why the perfectly correlated electron spins in the direction of measurements could not have been determined at the time of the initial entanglement preparation, with one spin up and the other down in the particular direction of measurements. Some physicists say that the electron spins would have to have been defined in all three dimensions - x-spin, y-spin, and z-spin. But this is impossible.
Bohm in 1951 and Bohm and Aharonov in 1957 argued that electron spins could be defined in at most a single direction, and this direction would very likely not be the random freely chosen direction of the experimenters. This is a serious misunderstanding...
Here, the investigator can measure either the x, y, or z component of the spin of article No.1, but not more than one of these components, in any particular experiment. Nevertheless, it still turns out as we shall see that whichever component is measured, the results are correlated, so that if the same component of the spin of No.2 is measured, it will always turn out to have the opposite value. This means that a measurement of any component of the spin of atom No.1 provides, as in classical theory, an indirect measurement of atom No.2. Since, by hypothesis, the two particles no longer interact, we have obtained a way of measuring an arbitrary component of the spin of particle No.2 without in any way disturbing that particle. Since this can be accomplished without in any way disturbing the second atom, we conclude that...precisely defined elements of reality must exist in the second atom, corresponding to the simultaneous definition of all three components of its spin. [This is a gravely flawed conclusion. It is not that components of spin are defined in all (3) direction, but that total spin zero means the spins will be found with opposite values in whatever agreed-upon direction they are measured!] ...Because the wave function can specify, at most, only one of these components at a time with complete precision, we are then led to the conclusion that the wave function does not provide a complete description of all elements of reality existing in the second atom. [The spherically symmetric (singlet state) wave function actually has no preferred direction, so as long as measurements are made symmetrically by the Stern-Gerlach devices, the atoms will be found to have perfectly correlated opposite spin values in that direction (which the observers must freely choose by previous agreement to be in the same direction, otherwise correlations will be reduced by the square of the cosine of the angle between them.]In 1957, Bohm and Aharonov expanded this description... In quantum theory, a difficulty arises, in the interpretation of the above experiment, because only one component of the spin of each particle can have a definite value at a given time. Thus, if the x component is definite, then the y and z components are indeterminate and we may regard them more or less as in a kind of random fluctuation.But having opposite spins in even a single preferred direction would not explain the experimental data! Had there been a single preferred direction (or angle) for electron spins in the initial entanglement preparation, there is essentially zero chance that Alice and Bob could observe in precisely that (unknown) direction or angle. And observations at angle θ to that initial preferred direction will produce decorrelated results + + and - - proportional to sin2θ.
Part 6 No Preferred Direction in the Spherically Symmetric Wave Function
No preferred direction exists in the initial entanglement preparation. The original entangled state with total spin angular momentum zero is rotationally and spherically symmetric, the same in all directions. The arbitrary direction of measurement or angle for Alice and Bob is introduced by them, agreed to before they measure! Total spin angular momentum is conserved as zero at all times from the initial entanglement to their measurements (assuming that no environmental interaction disturbs either particle).
As long as Alice and Bob now measure in the same plane (same direction, same angle), a new planar symmetry replaces the spherical symmetry and defines the one component of electron spin that Bohm and Aharonov say is allowed. The conservation of total spin angular momentum zero continues. As long as Alice and Bob measure in their "freely chosen" plane (preserving the symmetry), conservation of total spin angular momentum continues. There are no "local hidden variables" traveling with the particles to maintain perfect correlations, but conserved total spin zero might be called a "hidden constant of the motion" that provides the needed "common cause" for the correlations.
Part 7 John Bell and his Inequalities Theorem
We examine John Bell's theorem predicting how correlations between measurements made at differing angles could distinguish between local hidden variables and quantum mechanics. Bell predicted how the correlations would be reduced if Alice and Bob did not measure in the same direction, but chose measurement angles different by θ degrees. And we will examine Bell's hypothesis about how the falloff of correlations with increasing angle θ is different for local hidden variables (a straight line function of θ) and for quantum mechanics (a curved cosθ function).
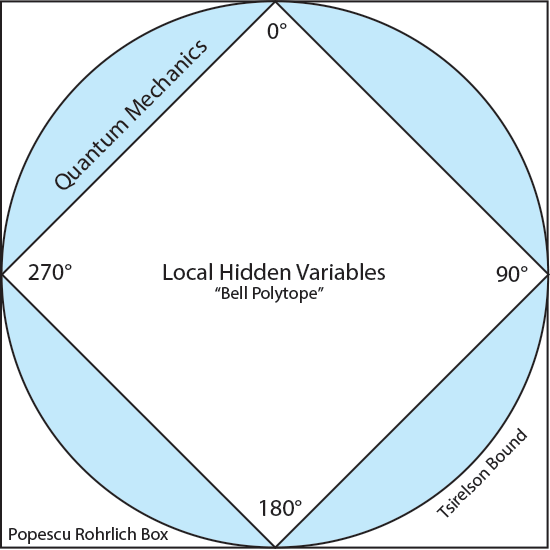 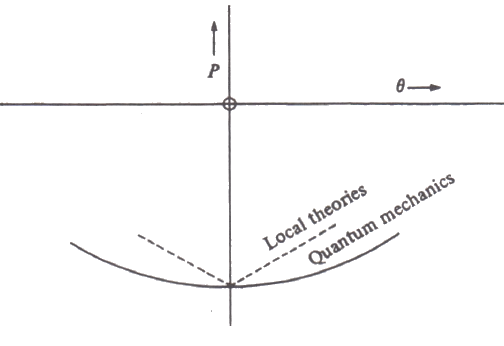 Unlike the quantum correlation, which is stationary in θ at θ = 0, at the hidden variable correlation must have a kink thereIn his famous 1981 article on "Bertlmann's Socks," Bell explains that the predictions for his "ad hoc" model are linear in the angle difference |a - b|, and he notes the fact that his inequality only agrees with the quantum predictions at the corners of the square of linear predictions above, and not at intermediate angles. To account then for the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen-Bohm correlations we have only to assume that the two particles emitted by the source have oppositely directed magnetic axes. Then if the magnetic axis of one particle is more nearly along (than against) one Stern-Gerlach field, the magnetic axes of the other particle will be more nearly against (than along) a parallel Stern- Gerlach field. So when one particle is deflected up, the other is deflected down, and vice versa. There is nothing whatever problematic or mind-boggling about these correlations, with parallel Stern-Gerlach analyzers, from the Einsteinian point of view. So far so good. But now go a little further than before, and consider non-parallel Stern-Gerlach magnets. Let the first be rotated away from some standard position, about the particle line of flight, by an angle a. Let the second be rotated likewise by an angle b. Then if the magnetic axis of either particle separately is randomly oriented, but if the axes of the particles of a given pair are always oppositely oriented, a short calculation gives for the probabilities of the various possible results, in the ad hoc model,... P(up, down) = P(down, up) = 1/2 - |a-b|/2π where ‘up’ and ‘down’ are defined with respect to the magnetic fields of the two magnets. However, a quantum mechanical calculation gives P(up, down) = P(down, up) = 1/2 - 1/2(sin(a - b)/2)2 [= 1/2(cos(a - b)/2)2] Thus the ad hoc model does what is required of it (i.e., reproduces quantum mechanical results) only at (a — b) = 0, (a - b) = π/2 and (a — b) = π, but not at intermediate angles.What was Bell's "short calculation" that gives "the probabilities of possible results" in his ad hoc model as linearly proportional to the angle |a-b|? Bell does not give us any underlying physical reasons for the linear dependence on angle. He clearly knows that his linear "inequality" is a strong challenge to the curved cosine prediction of quantum mechanics. And Bell's odd prediction of sharp corners or "kinks" where his straight lines turn ninety degrees (it is only at these corners where his linear inequality agrees with the curving quantum mechanics), surely should have prompted Bell to give us a deeper physical explanation of his theorem? And what exactly was Bell's "quantum mechanical calculation" that gives us probabilities proportional to the cosine of the angle |a-b| squared? This more physical picture coincides with falloff of light polarization when polarizers are crossed at an angle (Malus's Law). Conservation of total spin angular momentum zero (our "hidden constant of the motion") perfectly matches Bell's quantum mechanics predictions.
Part 8 Were the Correlations Predetermined?
Could the measurement outcomes have been predetermined at the initial entanglement?
John Bell considered this a possibility. In his very first paper on EPR, he wrote...
Since we can predict in advance the result of measuring any chosen component of σ2, by previously measuring the same component of σ1, it follows that the result of any such measurement must actually be predetermined. Since the initial quantum mechanical wave function does not determine the result of an individual measurement, this predetermination implies the possibility of a more complete specification of the state.Over a decade later, Bell still considered predeterminism... Some people find this situation paradoxical. They may, for example, have come to think of quantum mechanics as fundamentally indeterministic. In particular they may have come to think of the result of a spin measurement on an unpolarized particle (and each particle, considered separately, is unpolarized here) as utterly indefinite until it has happened. And yet here is a situation where the result of such a measurement is perfectly definitely known in advance.During a mid-1980's interview by BBC Radio 3 organized by P. C. W. Davies and J. R. Brown, Bell proposed the idea of a "superdeterminism" that could explain the correlation of results in two-particle experiments without the need for faster-than-light signaling. The two experiments need only have been pre-determined by causes reaching both experiments from an earlier time. I was going to ask whether it is still possible to maintain, in the light of experimental experience, the idea of a deterministic universe? You know, one of the ways of understanding this business is to say that the world is super-deterministic. That not only is inanimate nature deterministic, but we, the experimenters who imagine we can choose to do one experiment rather than another, are also determined. If so, the difficulty which this experimental result creates disappears. Free will is an illusion - that gets us out of the crisis, does it? That's correct. In the analysis it is assumed that free will is genuine, and as a result of that one finds that the intervention of the experimenter at one point has to have consequences at a remote point, in a way that influences restricted by the finite velocity of light would not permit. If the experimenter is not free to make this intervention, if that also is determined in advance, the difficulty disappears.The freely chosen direction of measurement angle previously agreed upon by Alice and Bob can only be implemented at the time of their measurements and not before. As shown in parts 5 and 6, the only dependence on the original entanglement is that its spherically symmetric singlet state has total spin zero and no preferred direction. The specific measurement direction/angle, freely chosen by Alice and Bob, and the specific correlations at that measurement angle (specifically either + - or - +), results from the "collapse" of the Dirac/Schrödinger two-particle wave function (a "superposition" of + - and - + states) one of those states which is randomly realized. These random results are "created" long after the particles were together at entanglement, when the particles have apparently become "separated" by arbitrarily large distances. The phenomenon therefore appears distinctly "nonlocal," but it does not involve any physical interaction or information transfer between the particles. It is "caused" by a condition (the conserved total spin angular momentum zero) that has been true from the moment of initial entanglement, as long as neither particle is disturbed by any asymmetric environmental interaction.
Part 9 Do Spins Found Correlated in One Direction Mean Correlated in All?
In his 1951 textbook Quantum Theory, Bohm wrote...
Suppose that we have a molecule containing two atoms in a state in which the total spin is zero and that the spin of each atom is ℏ/2. Roughly speaking, this means that the spin of each atom points in a direction exactly opposite to that of the other, insofar as the spin may be said to have any definite direction at all. [Indeed, we can only say that the total spin zero of the two atoms means that their two-particle wave function ψ12 is spherically symmetric with no preferred direction - the singlet state.] Now suppose that the molecule is disintegrated by some process that does not change the total angular momentum. The two atoms will begin to separate and will soon cease to interact appreciably. [But Erwin Schrödinger tells us that they will not become independent and "cease to interact" until some measurement disentangles them, decohering their phases, and allowing their two-particle wave function ψ12 to be replaced with the product of two single-particle wave functions ψ12ψ2 or ψ2ψ1.] Their combined spin angular momentum, however, remains equal to zero, because no torques have acted on the system... Suppose now that one measures the spin angular momentum of any one of the particles, say No.1. Because of the existence of correlations we can immediately conclude that the angular momentum vector of the other particle (No.2) is equal and opposite to that on No.1. In this way, we can indirectly measure the angular momentum of particle No.2 by measuring the corresponding vector of particle No.1.The Bohm and Aharonov argument that perfectly opposed spins at the time of the Alice and Bob measurements (and in the arbitrary direction chosen by them) would require that the spins would have to be defined in all three axial directions (which is impossible). This is a flawed argument. When spins are measured in one direction, they are necessarily undefined in the other two directions, as Bohm and Aharonov later said. The original entangled state with total spin zero is rotationally symmetric, with no preferred direction, so that the preferred plane or direction of measurement for Alice and Bob is introduced by them. This symmetry ensures the conservation of total angular momentum zero until the time of measurement. As long as Alice and Bob measure in the same plane (preserving the symmetry), they maintain the conservation of angular momentum, our proposed "hidden constant of the motion."
Part 10 Physicists Who May Have Seen Conservation Principles
We review the work of some physicists to show they were clearly using conservation principles to explain some aspects of entanglement, but without their necessarily seeing how conservation of linear or angular momentum could produce the appearance of Einstein's "spooky action at a distance" without any interaction or "influence" between the particles.
David Bohm
Bohm and his Israeli student Yakir Aharonov reformulated the original EPR argument in terms of electron spin. They said experimental tests with continuous variables would be much more difficult than tests with discrete quantities, such as the spin of electrons or polarization of photons.
Bohm and Aharonov described the preparation of two particles, such that a measurement of one at a later time determines a measurement in the same direction of the other particle at any distance away.
We consider a molecule of total spin zero consisting of two atoms, each of spin one-half. The wave function of the system is thereforeTheir statement "because the total spin is still zero, it can immediately be concluded that the same component of the spin of the other particle (B) is opposite to that of A." surely is true because of the conservation of spin angular momentum.
Eugene Wigner
In an important article written after Bohm and before Bell's 1964 "theorem" paper, Eugene Wigner in 1963 said very clearly that the symmetrically placed positions (for the EPR paper) are caused by conservation of linear momentum and the perfectly opposite electron spins (for David Bohm's version of nonlocality with electrons) are the result of conservation of angular momentum. Wigner wrote
If a measurement of the momentum of one of the particles is carried out — the possibility of this is never questioned — and gives the result p, the state vector of the other particle suddenly becomes a (slightly damped) plane wave with the momentum -p. This statement is synonymous with the statement that a measurement of the momentum of the second particle would give the result -p, as follows from the conservation law for linear momentum. The same conclusion can be arrived at also by a formal calculation of the possible results of a joint measurement of the momenta of the two particles. One can go even further: instead of measuring the linear momentum of one particle, one can measure its angular momentum about a fixed axis. If this measurement yields the value mℏ, the state vector of the other particle suddenly becomes a cylindrical wave for which the same component of the angular momentum is -mℏ. This statement is again synonymous with the statement that a measurement of the said component of the angular momentum of the second particle certainly would give the value -mℏ. This can be inferred again from the conservation law of the angular momentum (which is zero for the two particles together) or by means of a formal analysis. 8
John Bell
We can ask why John Bell, with the prior writings of Bohm and Wigner, never explicitly considered the conservation of linear momentum in the EPR experiment, and conservation of spin angular momentum as explaining the perfectly opposite electron spins found in Bohm's version of EPR. But we can see in Bell's description that, like Bohm, he is implicitly using conservation of angular momentum.
In his 1964 paper "On the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen Paradox," Bell made the case for nonlocality.
With the example advocated by Bohm and Aharonov, the EPR argument is the following. Consider a pair of spin one-half particles formed somehow in the singlet spin state and moving freely in opposite directions. Measurements can be made, say by Stern-Gerlach magnets, on selected components of the spins σ1 and σ2. If measurement of the component σ1 • a, where a is some unit vector, yields the value + 1 then, according to quantum mechanics, measurement of σ2 • a must yield the value — 1 and vice versa.During a mid-1980's interview by BBC Radio 3 organized by P. C. W. Davies and J. R. Brown, Bell proposed the idea of a "superdeterminism" that could explain the correlation of results in two-particle experiments without the need for faster-than-light signaling. The two experiments need only have been pre-determined by causes reaching both experiments from an earlier time. I was going to ask whether it is still possible to maintain, in the light of experimental experience, the idea of a deterministic universe? You know, one of the ways of understanding this business is to say that the world is super-deterministic. That not only is inanimate nature deterministic, but we, the experimenters who imagine we can choose to do one experiment rather than another, are also determined. If so, the difficulty which this experimental result creates disappears.But the obvious fact that the total spin angular momentum at zero is conserved for all times since the initial entanglement means that the two particles are indeed "determined by causes reaching both experiments from an earlier time," though not "superdetermined from the origin of the universe.
C.S.Unnikrishnan
In 2005, C.S.Unnikrishnan of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research in Mumbai, India was an exception. He proposed explicitly that the conservation law of angular momentum can correlate measurements of entangled electrons, explaining the perfect correlations of entangled particles, without the faster-than-light interactions-at-a-distance or "hidden variables" often invoked to explain nonlocaiity.
Unnikrishnan wrote
Bell’s inequalities can be obeyed only by violating a conservation law.Unnikrishnan argues that conservation of angular momentum (electron spin) produces the same perfect correlations (or anti-correlations) found in all Bell test experiments when both experimenters measure at the same (pre-agreed upon) measurement angle. However, Unnikrishnan is concerned that "for individual measurements of the two-point correlation, the conservation law cannot be invoked, since only the conditional probabilities are predicted by quantum mechanics." He uses instead averages of measurements. Unnikrishnan's apparent concern is that individual measurements will have random outcomes of up-down, down-up, and possibly even some up-up and down-down. He mistakenly thinks quantum mechanics predicts separate probabilities for each electron. The latter two product states (up-up and down-down) would violate conservation of angular momentum.
Part 11 Conservation Laws and Constants of the Motion
Conservation laws are the consequence of extremely deep properties of nature that arise from simple considerations of symmetry. We regard these laws as "cosmological principles." Physical laws do not depend on the absolute place and time of experiments, nor their particular direction in space. Conservation of linear momentum depends on the translation invariance of physical systems, conservation of energy the independence of time, and conservation of angular momentum the invariance under rotations. Conservation laws are the consequence of these spatial symmetries, as explained by Emmy Noether.
David Bohm's version of the EPR experiment starts with two electrons (or photons) prepared in an entangled state that is a superposition of two-particle states, each of which conserves the total angular momentum and, of course, conserves the linear momentum as in Einstein's original EPR example.
Quantum mechanics describes the probability amplitude wave function Ψ12 of the two-particle system as in a superposition of two-particle states. It is not a product of single-particle states, as Erwin Schrödinger told Einstein in his reaction to the EPR paper. We can write this as
Ψ12 = 1/√2) | 1+2- > + 1/√2) | 1-2+ > (1)
The probability amplitude wave function Ψ12 travels away from the source (at the speed of light or less). The total spin zero wave function is rotationally symmetric and isotropic, the same in all directions.
Let's assume that at t0 an observer finds a particle with spin up in the x direction. This measurement breaks the rotational symmetry. The new symmetry is planar, including the chosen x direction and the z direction back to the origin of the entangled particles.
Before the measurement, the spin has a possibility of being found in any direction. Rotational symmetry says the probability is the same in all directions. This does not mean a particle has spins in all directions at all times, which is impossible.
At the time of this "first" measurement, say by observer A, new information comes into existence telling us that the wave function Ψ12 has "collapsed" into the state | 1+2- >. Probabilities have now become certainties, one possibility is now an actuality. If the first measurement finds particle 1's x-component spin is up, so the same spin component of entangled particle 2 must be down to conserve total angular momentum.
And conservation of linear momentum tells us that at t0 the second electron is equidistant from the source in the opposite direction.
As with any wave-function "collapse", the probability amplitude information changes. Nothing really "collapses." Nothing physical, no matter or energy, is moving. Only information is changing. The wave function is updated to reflect the new information that comes into existence as the result of the measurement.
When the "first" measurement finds particle 1 as spin-up at t0, at that moment of new information creation, particle 2 will be found (if measured simultaneously or later) in a spin-down state with probability unity (certainty). And the results of observer B's measurement at t0 or any later time t1 is therefore determined to be spin down (if and only if, B measures in a pre-agreed upon same direction).
Notice that Einstein's intuition that observer B's result seems already "determined" or "fixed" before the second measurement is in fact correct. Observer B's outcome is determined by the law of conservation of momentum.
But the measurement by observer B was not pre-determined before observer A's measurement. It was simply determined by her measurement. The measured values of particle 1 spin-up and particle 2 spin-down did not exist before the "free choice" of observer A brought them into existence, as Werner Heisenberg insisted.
Which of the two-particle quantum states | + - > or | - + > occurs is completely random. It is the result of "Nature's choice," as Paul Dirac described it.
Note also that before the measurement the two-particle wave function was rotationally symmetric. No preferred angular direction existed. The preferred angle also comes into existence as a result of what Heisenberg called the "free choice" of the ("first") experimenter. Of course neither Alice nor Bob measures first, as their measurements of a single entangled pair reaching their experiments are normally made simultaneously.
This "free choice" of a measurement angle breaks the rotational symmetry of the original two-particle wave function. As Erwin Schrödinger described it to Einstein in his 1935 response to the EPR paper, the measurement disentangles the particles and projects the pure-state superposition into a mixed-state product of single-particle wave functions, either | + - > or | - + >. Many critics have pointed out that the two particles cannot already have opposite spin values in a specific direction long before the measurements. That would require them to have spin values in all three x, y, and z directions, say some physicists (e.g., David Bohm) which is impossible, they say. They only need to acquire opposite spins when measured along an agreed upon direction that breaks the rotational symmetry of the two-particle wave function. Finally note that conservation of total spin zero requires no instantaeous superluminal influence or interaction by one particle on the other. It only requires that interactions between the particles preserve the symmetry needed for the conservation law. Many other critics have insisted that some mechanism will be found to explain the mysterious entanglement That symmetry has become linear and planar, as the rotational symmetry disappears, leaving symmetry only along the plane between the electrons that includes the chosen measurement direction. If the two particles did not conserve total spin zero (and every Bell test shows that they do conserve total spin), the violation of the angular momentum conservation law would likely be met with more criticism than hypothetical superluminal interactions, which are of course impossible. What about the uncertainty principle? In the case of EPR measuring the position x (or the momentum p) of the two particles, won't their values be "fuzzy" (ΔxΔp ~ħ) and therefore not conserve momentum exactly, but only statistically for large numbers of examples? No, the conservation laws require that if x1 is found less than the expected value by an amount -δ, that x2 would be greater by the opposite amount +δ, so that the two particles are equidistant from the origin. This ensures the conservation of linear momentum, just as Einstein in 1924 proved that the Bohr-Kramers-Slater theory that energy is only conserved statistically was wrong. Momentum is conserved exactly in every measurement, although the uncertainty principle may prevent this from being shown experimentally. Furthermore, in the Bohm version of nonlocality the quantities are discrete spins, not continuous positions or momenta. Electron spins are always measured to be either up or down, with nothing fuzzy about these values. And all the experimental results from all the Bell tests have always found the two spins opposite as long as both measurements are made in exactly the same direction, thus conserving total spin zero. There is still indeterminism (uncertainty) in the spin measurement results. We don't know which electron will be up and which down. It is this property that "does not exist" before the measurement. Physics has not found any hidden variables, local or nonlocal, as the cause of the perfect opposite spins. Is the conserved total spin zero acceptable as what we call a "hidden constant of the motion" that completely accounts for the perfectly opposite spins?
Part 12 David Mermin's Instruction Sets as Hidden Variables
We trace the modern idea of "instruction sets" accompanying the particles as "hidden variables" to Erwin Schrödinger's suggestion that the particles seem to know the answers to all possible questions that would be asked of them when measured. What process could prepare such information for the particles and what mechanism could read the information in the "instructions" and then change the particle properties as required?
In his 1936 paper "Property Relations Between Separated Systems," Schrödinger wrote
Years ago I pointed out that when two systems separate far enough to make it possible to experiment on one of them without interfering with the other, they are bound to pass, during the process of separation, through stages which were beyond the range of quantum mechanics as it stood then...Schrödinger refers to the central claim of the EPR paradox, in terms of the information available to the particles... the result of measuring p1 serves to predict the result for p2 and vice versa. But of course every one of the four observations in question, when actually performed, disentangles the systems, furnishing each of them with an independent representative of its own. A second observation, whatever it is and on whichever system it is executed, produces no further change in the representative of the other system. Yet since I can predict either x1 or p1 without interfering with system No. 1 and since system No. 1, like a scholar in examination, cannot possibly know which of the two questions I am going to ask it first: it so seems that our scholar is prepared to give the right answer to the first question he is asked, anyhow. Therefore he must know both answers; which is an amazing knowledge.
Part 13. Summary of the "Hidden Constant" hypothesis
Standard quantum mechanics plus the principle of angular momentum conservation (true for quantum and classical mechanics) predicts:
Ψ12 = 1/√2) | 1+2- > + 1/√2) | 1-2+ > (1)
will become a mixture of product states that have decohered(their pure-state coherent phase relations lost). They are disentangled, as Erwin Schrödinger argued in 1936. Measuring one can still tell us something about the other. he said. But they have decohered and can no longer interfere with one another and cannot remain correlated after future measurements. They have then truly separated and "independent," but they had not become independent before the disentanglement, as Einstein had hoped with his separability principle (Trennungsprinzip).
References
|