|
Topics
Introduction
Problems Freedom Knowledge Mind Life Chance Quantum Entanglement Scandals Philosophers Mortimer Adler Rogers Albritton Alexander of Aphrodisias Samuel Alexander William Alston Anaximander G.E.M.Anscombe Anselm Louise Antony Thomas Aquinas Aristotle David Armstrong Harald Atmanspacher Robert Audi Augustine J.L.Austin A.J.Ayer Alexander Bain Mark Balaguer Jeffrey Barrett William Barrett William Belsham Henri Bergson George Berkeley Isaiah Berlin Richard J. Bernstein Bernard Berofsky Robert Bishop Max Black Susan Blackmore Susanne Bobzien Emil du Bois-Reymond Hilary Bok Laurence BonJour George Boole Émile Boutroux Daniel Boyd F.H.Bradley C.D.Broad Michael Burke Jeremy Butterfield Lawrence Cahoone C.A.Campbell Joseph Keim Campbell Rudolf Carnap Carneades Nancy Cartwright Gregg Caruso Ernst Cassirer David Chalmers Roderick Chisholm Chrysippus Cicero Tom Clark Randolph Clarke Samuel Clarke Anthony Collins August Compte Antonella Corradini Diodorus Cronus Jonathan Dancy Donald Davidson Mario De Caro Democritus William Dembski Brendan Dempsey Daniel Dennett Jacques Derrida René Descartes Richard Double Fred Dretske Curt Ducasse John Earman Laura Waddell Ekstrom Epictetus Epicurus Austin Farrer Herbert Feigl Arthur Fine John Martin Fischer Frederic Fitch Owen Flanagan Luciano Floridi Philippa Foot Alfred Fouilleé Harry Frankfurt Richard L. Franklin Bas van Fraassen Michael Frede Gottlob Frege Peter Geach Edmund Gettier Carl Ginet Alvin Goldman Gorgias Nicholas St. John Green Niels Henrik Gregersen H.Paul Grice Ian Hacking Ishtiyaque Haji Stuart Hampshire W.F.R.Hardie Sam Harris William Hasker R.M.Hare Georg W.F. Hegel Martin Heidegger Heraclitus R.E.Hobart Thomas Hobbes David Hodgson Shadsworth Hodgson Baron d'Holbach Ted Honderich Pamela Huby David Hume Ferenc Huoranszki Frank Jackson William James Lord Kames Robert Kane Immanuel Kant Tomis Kapitan Walter Kaufmann Jaegwon Kim William King Hilary Kornblith Christine Korsgaard Saul Kripke Thomas Kuhn Andrea Lavazza James Ladyman Christoph Lehner Keith Lehrer Gottfried Leibniz Jules Lequyer Leucippus Michael Levin Joseph Levine George Henry Lewes C.I.Lewis David Lewis Peter Lipton C. Lloyd Morgan John Locke Michael Lockwood Arthur O. Lovejoy E. Jonathan Lowe John R. Lucas Lucretius Alasdair MacIntyre Ruth Barcan Marcus Tim Maudlin James Martineau Nicholas Maxwell Storrs McCall Hugh McCann Colin McGinn Michael McKenna Brian McLaughlin John McTaggart Paul E. Meehl Uwe Meixner Alfred Mele Trenton Merricks John Stuart Mill Dickinson Miller G.E.Moore Ernest Nagel Thomas Nagel Otto Neurath Friedrich Nietzsche John Norton P.H.Nowell-Smith Robert Nozick William of Ockham Timothy O'Connor Parmenides David F. Pears Charles Sanders Peirce Derk Pereboom Steven Pinker U.T.Place Plato Karl Popper Porphyry Huw Price H.A.Prichard Protagoras Hilary Putnam Willard van Orman Quine Frank Ramsey Ayn Rand Michael Rea Thomas Reid Charles Renouvier Nicholas Rescher C.W.Rietdijk Richard Rorty Josiah Royce Bertrand Russell Paul Russell Gilbert Ryle Jean-Paul Sartre Kenneth Sayre T.M.Scanlon Moritz Schlick John Duns Scotus Albert Schweitzer Arthur Schopenhauer John Searle Wilfrid Sellars David Shiang Alan Sidelle Ted Sider Henry Sidgwick Walter Sinnott-Armstrong Peter Slezak J.J.C.Smart Saul Smilansky Michael Smith Baruch Spinoza L. Susan Stebbing Isabelle Stengers George F. Stout Galen Strawson Peter Strawson Eleonore Stump Francisco Suárez Richard Taylor Kevin Timpe Mark Twain Peter Unger Peter van Inwagen Manuel Vargas John Venn Kadri Vihvelin Voltaire G.H. von Wright David Foster Wallace R. Jay Wallace W.G.Ward Ted Warfield Roy Weatherford C.F. von Weizsäcker William Whewell Alfred North Whitehead David Widerker David Wiggins Bernard Williams Timothy Williamson Ludwig Wittgenstein Susan Wolf Xenophon Scientists David Albert Philip W. Anderson Michael Arbib Bobby Azarian Walter Baade Bernard Baars Jeffrey Bada Leslie Ballentine Marcello Barbieri Jacob Barandes Julian Barbour Horace Barlow Gregory Bateson Jakob Bekenstein John S. Bell Mara Beller Charles Bennett Ludwig von Bertalanffy Susan Blackmore Margaret Boden David Bohm Niels Bohr Ludwig Boltzmann John Tyler Bonner Emile Borel Max Born Satyendra Nath Bose Walther Bothe Jean Bricmont Hans Briegel Leon Brillouin Daniel Brooks Stephen Brush Henry Thomas Buckle S. H. Burbury Melvin Calvin William Calvin Donald Campbell John O. Campbell Sadi Carnot Sean B. Carroll Anthony Cashmore Eric Chaisson Gregory Chaitin Jean-Pierre Changeux Rudolf Clausius Arthur Holly Compton John Conway Simon Conway-Morris Peter Corning George Cowan Jerry Coyne John Cramer Francis Crick E. P. Culverwell Antonio Damasio Olivier Darrigol Charles Darwin Paul Davies Richard Dawkins Terrence Deacon Lüder Deecke Richard Dedekind Louis de Broglie Stanislas Dehaene Max Delbrück Abraham de Moivre David Depew Bernard d'Espagnat Paul Dirac Theodosius Dobzhansky Hans Driesch John Dupré John Eccles Arthur Stanley Eddington Gerald Edelman Paul Ehrenfest Manfred Eigen Albert Einstein George F. R. Ellis Walter Elsasser Hugh Everett, III Franz Exner Richard Feynman R. A. Fisher David Foster Joseph Fourier George Fox Philipp Frank Steven Frautschi Edward Fredkin Augustin-Jean Fresnel Karl Friston Benjamin Gal-Or Howard Gardner Lila Gatlin Michael Gazzaniga Nicholas Georgescu-Roegen GianCarlo Ghirardi J. Willard Gibbs James J. Gibson Nicolas Gisin Paul Glimcher Thomas Gold A. O. Gomes Brian Goodwin Julian Gough Joshua Greene Dirk ter Haar Jacques Hadamard Mark Hadley Ernst Haeckel Patrick Haggard J. B. S. Haldane Stuart Hameroff Augustin Hamon Sam Harris Ralph Hartley Hyman Hartman Jeff Hawkins John-Dylan Haynes Donald Hebb Martin Heisenberg Werner Heisenberg Hermann von Helmholtz Grete Hermann John Herschel Francis Heylighen Basil Hiley Art Hobson Jesper Hoffmeyer John Holland Don Howard John H. Jackson Ray Jackendoff Roman Jakobson E. T. Jaynes William Stanley Jevons Pascual Jordan Eric Kandel Ruth E. Kastner Stuart Kauffman Martin J. Klein William R. Klemm Christof Koch Simon Kochen Hans Kornhuber Stephen Kosslyn Daniel Koshland Ladislav Kovàč Leopold Kronecker Bernd-Olaf Küppers Rolf Landauer Alfred Landé Pierre-Simon Laplace Karl Lashley David Layzer Joseph LeDoux Gerald Lettvin Michael Levin Gilbert Lewis Benjamin Libet David Lindley Seth Lloyd Werner Loewenstein Hendrik Lorentz Josef Loschmidt Alfred Lotka Ernst Mach Donald MacKay Henry Margenau Lynn Margulis Owen Maroney David Marr Humberto Maturana James Clerk Maxwell John Maynard Smith Ernst Mayr John McCarthy Barbara McClintock Warren McCulloch N. David Mermin George Miller Stanley Miller Ulrich Mohrhoff Jacques Monod Vernon Mountcastle Gerd B. Müller Emmy Noether Denis Noble Donald Norman Travis Norsen Howard T. Odum Alexander Oparin Abraham Pais Howard Pattee Wolfgang Pauli Massimo Pauri Wilder Penfield Roger Penrose Massimo Pigliucci Steven Pinker Colin Pittendrigh Walter Pitts Max Planck Susan Pockett Henri Poincaré Michael Polanyi Daniel Pollen Ilya Prigogine Hans Primas Giulio Prisco Zenon Pylyshyn Henry Quastler Adolphe Quételet Pasco Rakic Nicolas Rashevsky Lord Rayleigh Frederick Reif Jürgen Renn Giacomo Rizzolati A.A. Roback Emil Roduner Juan Roederer Robert Rosen Frank Rosenblatt Jerome Rothstein David Ruelle David Rumelhart Michael Ruse Stanley Salthe Robert Sapolsky Tilman Sauer Ferdinand de Saussure Jürgen Schmidhuber Erwin Schrödinger Aaron Schurger Sebastian Seung Thomas Sebeok Franco Selleri Claude Shannon James A. Shapiro Charles Sherrington Abner Shimony Herbert Simon Dean Keith Simonton Edmund Sinnott B. F. Skinner Lee Smolin Ray Solomonoff Herbert Spencer Roger Sperry John Stachel Kenneth Stanley Henry Stapp Ian Stewart Tom Stonier Antoine Suarez Leonard Susskind Leo Szilard Max Tegmark Teilhard de Chardin Libb Thims William Thomson (Kelvin) Richard Tolman Giulio Tononi Peter Tse Alan Turing Robert Ulanowicz C. S. Unnikrishnan Nico van Kampen Francisco Varela Vlatko Vedral Vladimir Vernadsky Clément Vidal Mikhail Volkenstein Heinz von Foerster Richard von Mises John von Neumann Jakob von Uexküll C. H. Waddington Sara Imari Walker James D. Watson John B. Watson Daniel Wegner Steven Weinberg August Weismann Paul A. Weiss Herman Weyl John Wheeler Jeffrey Wicken Wilhelm Wien Norbert Wiener Eugene Wigner E. O. Wiley E. O. Wilson Günther Witzany Carl Woese Stephen Wolfram H. Dieter Zeh Semir Zeki Ernst Zermelo Wojciech Zurek Konrad Zuse Fritz Zwicky Presentations ABCD Harvard (ppt) Biosemiotics Free Will Mental Causation James Symposium CCS25 Talk Evo Devo September 12 Evo Devo October 2 Evo Devo Goodness Evo Devo Davies Nov12 |
Disentanglement and the Bell Inequalities
In the year following the Einstein-Podsky-Rosen paper, Erwin Schrödinger looked more carefully at Einstein's "separability" assumption (Trennungsprinzip) that an entangled system can be separated enough to be regarded as two systems with independent wave functions:
Years ago I pointed out that when two systems separate far enough to make it possible to experiment on one of them without interfering with the other, they are bound to pass, during the process of separation, through stages which were beyond the range of quantum mechanics as it stood then. For it seems hard to imagine a complete separation, whilst the systems are still so close to each other, that, from the classical point of view, their interaction could still be described as an unretarded actio in distans. And ordinary quantum mechanics, on account of its thoroughly unrelativistic character, really only deals with the actio in distans case. The whole system (comprising in our case both systems) has to be small enough to be able to neglect the time that light takes to travel across the system, compared with such periods of the system as are essentially involved in the changes that take place...Schrödinger says that the entangled system may become disentangled (Einstein's separation) and yet some perfect correlations between later measurements might remain. Note that the entangled system could simply decohere as a result of interactions with the environment, as proposed by decoherence theorists. The perfectly correlated results of Bell-inequality experiments might nevertheless be preserved, depending on the interaction. Schrödinger tells us that the two-particle wave function Ψ12 will be separated into the product of single-particle wave functions Ψ1 and Ψ2 by a measurement of either particle, for example, by either Alice's or Bob's measurements in the case of Bell's Theorem, or by any interaction with the environment.
Bell's Theorem
Following David Bohm's version of EPR, John Bell considered two spin-1/2 particles in an entangled state with total spin zero.
| ψ > = (1/√2) | + - > - (1/√2) | - + > (1)
This is a superposition of two states, either of which conserves total spin zero. The minus sign ensures the state is anti-symmetric, changing sign under interchange of identical electrons. The coefficients 1/√2, when squared, give us the 1/2 probability of finding either state.
Schrödinger does not mention conservation principles, but he knows that EPR used them to gather knowledge about the second system by measurements on the first, as he accepts. Conservation principles are the deep reason for the perfect correlations between various observables, i.e., conservation of mass, energy, momentum, angular momentum, and in Bell's case spin.
Let's assume that Alice makes a measurement of a spin component of one particle, say the x-component. First, her measurement projects the entangled system randomly into either the | + - > or | - + > state. Alice measures + (spin up) or - (spin down). A succession of such random outcomes produces the bit string with "true randomness" (Gisin, 2014) or "really random" and "totally random" (Bub, 2016, 2018) that is needed for use as a quantum key code in quantum cryptography. If Alice measures the x-component and finds spin up, equation 1 becomes
| ψ > = | + - > (2)
Using Schrödinger's expansion of the two-particle wave function in products of single-particle wave functions, we can further write
| ψ > = | + >x | - >x (3)
Schrödinger describes the entangled system as having separated, disentangled into the product of independent single-particle wave functions | + >x and | - >x.
The two particles continue to evolve apart. But now we can say that future measurements of Alice's particle are determined to be found with the x-component of spin up (| + >x), and the x-component of Bob's particle spin down (| - >x), by conservation of angular momentum.
But Bob will find his particle spin down with certainty if and only if he measures at the same angle as Alice. If Bob measures at any other angle, the perfect anti-correlation that distributes perfectly matched quantum key pairs to Alice and Bob will be lost.
Bell's inequality was a study of how these perfect correlations decrease as a function of the angle between measurements by Alice and Bob. Bell predicted local hidden variables would produce a linear function of this angle, whereas, he said, quantum mechanics should produce a dependence on the cosine of this angle. As the angle changes, admixtures of other states will be found, for example | + + > in which Alice and Bob both measure spin up.
Bell wrote that "Since we can predict in advance the result of measuring any chosen component of σ2, by previously measuring the same component of σ1, it follows that the result of any such measurement must actually be predetermined."
David Bohm has shown that these values were not predetermined (they did not even exist according to the Copenhagen Interpretation) before Alice's measurement. According to Werner Heisenberg and Pascual Jordan, Alice's x-component of spin is created by Alice's measurement in the x-direction, the result of Alice's "free choice."
According to Paul Dirac, Alice's random x-component value depends on "Nature's choice," the source of what Nicolas Gisin (2014) calls the "true randomness" needed for quantum key distribution.
Many commentators on Bell's theorem claim that Alice and Bob's spin component values can not pre-exist their measurements, certainly not (as Bohm showed) from their initial preparation in the total spin-zero entangled state (1). In that case, spin component values would have to pre-exist in all three dimensions, they say.
In his landmark 1985 article "Is the moon there
when nobody looks? Reality and the quantum theory," David Mermin wrote "it [pre-existing spins] amounts to the insistence that each particle has stamped on it in advance the outcome of the measurements of three different spin components corresponding to noncommuting observables S·a(i), i = l,2, 3."
But Bohm showed that the single spin component in the x-direction is created when Alice measures the two-particle wave function ψ12 in the x-direction. Alice's measurement collapses ψ12 and disentangles/decoheres it into Schrödinger's product of single-particle wave functions, ψ1x and ψ2x ( | + >x and | - >x ). The nonlocal collapse of the two-particle wave function conserves the total spin zero, so that Bob's now-independent x-component of spin is precisely opposite to that of Alice.
And it is that same spin x-component that Bob must measure to get the perfect anti-correlations needed for quantum cryptography keys. The other two (unmeasured) spin components have no definite values. They are still in random superpositions (their overall rotational symmetry still ensuring conservation of angular momentum).
Indeed, should Bob measure a different angle from Alice, we get the angle-dependent results of the Bell inequalities. Bell predicted a linear fall-off for local hidden variables and a cosine squared dependence for quantum mechanics. But every experiment has confirmed the quantum mechanical dependence on the cosine of the angle between Alice's and Bob's measurements.
The cosine squared dependence of the intensity of light passing through crossed polarizers was discovered in 1809 by Étienne Louis Malus. It is known as the "law of Malus."
In the important case where Alice and Bob measure at the same angle, the cosine of zero is 1 and the correlation is perfect.
This corresponds to Paul Dirac's assertion that there are some cases where quantum mechanical experiments involve no indeterminism. Dirac mentions the case of measuring a photon passing through a vertical polarizer that has been prepared in a vertical state of polarization. The probability is unity or certainty, Dirac says.
Only when the initial state and the observation are such that there is a probability unity, i.e. a certainty, for one particular result is it possible that the observation may produce no change of state... The state of a system after a maximum observation has been made on it is such that there exists a maximum observation (namely, an immediate repetition of the maximum observation already made) which, when made on the system in this state, will for a certainty lead to one particular result (namely, the previous result over again).This is the origin of the quantum Zeno effect. We can visualize the angles in the Bell experiments that correspond to measuring the same angles, or directly opposite angles, which according to Dirac give equally certain outcomes. We can also show Bell's straight-line predictions for local hidden variables, the sides of the square of the local hidden variables "polytope." The certain outcomes are at the corners of the square, 0°, 90°, 180°, 270°, where Bell somewhat unrealistically predicted there would be "kinks" instead of the smooth curvature of the cosines at the corners that are predicted by quantum mechanics. 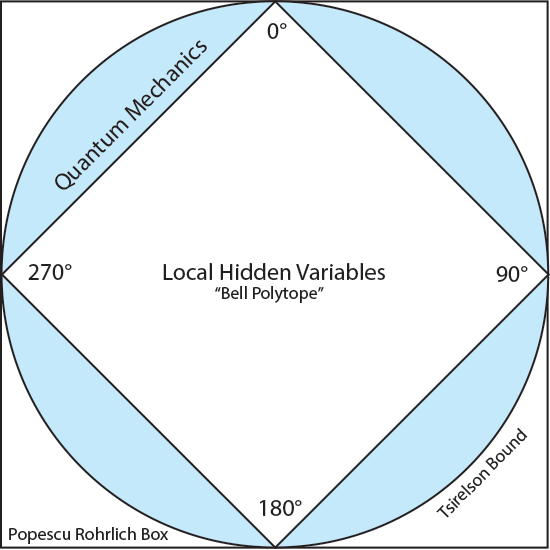 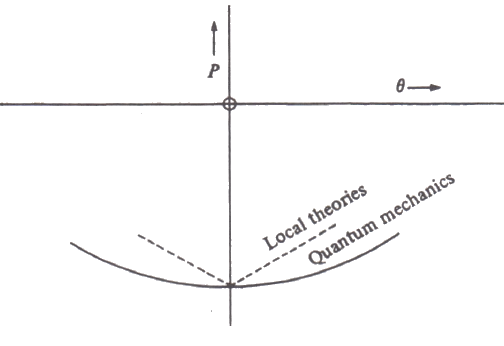 Unlike the quantum correlation, which is stationary in θ at θ = 0, at the hidden variable correlation must have a kink there.
Violating Tsirelson's Bound?
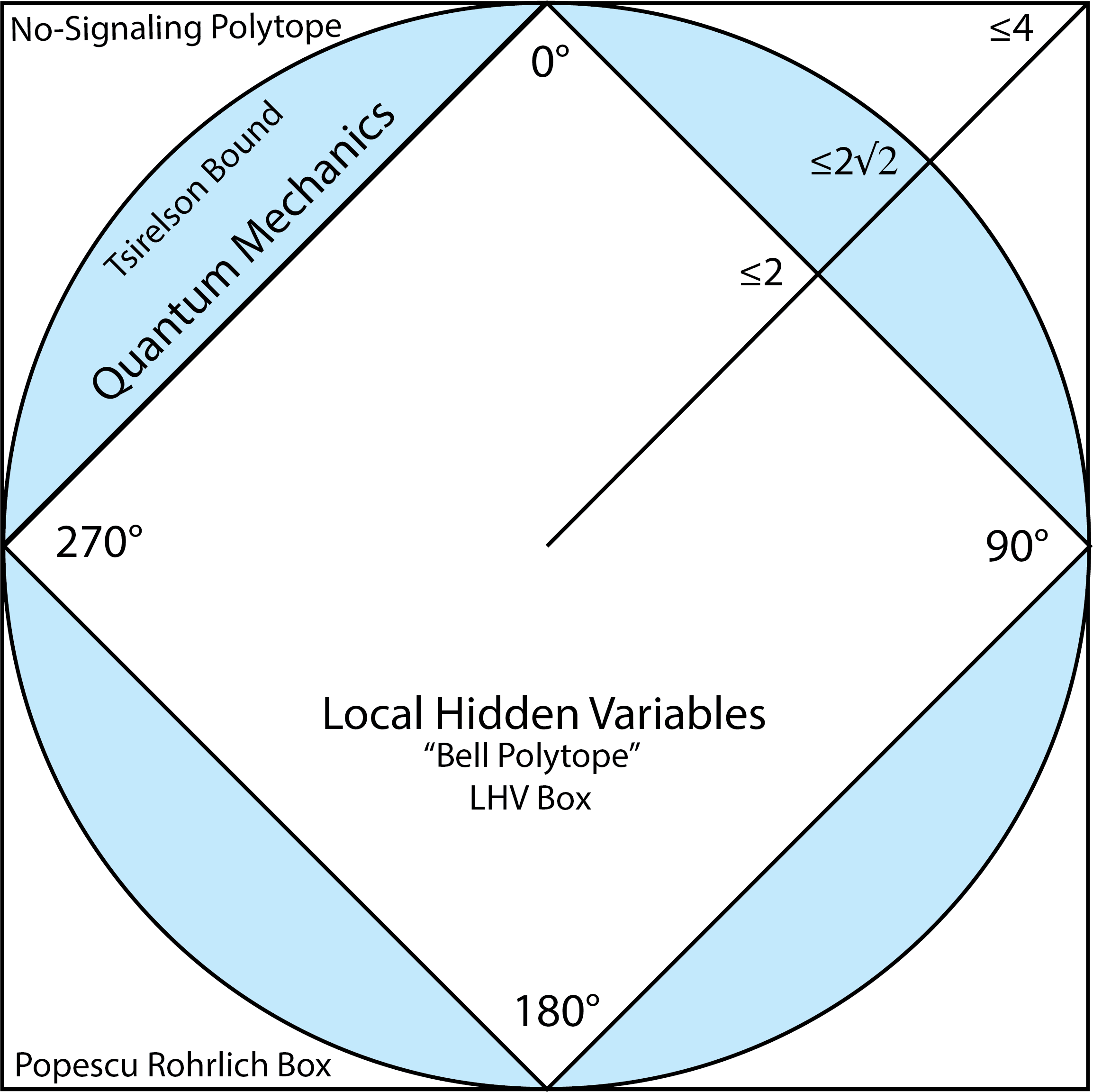 "The correlation function allowed by the basic assumption of validity of conservation law is unique, and surprisingly it is identical to the quantum mechanical correlation function. Therefore, a physical system with discrete observable values can show correlations different from what is predicted by quantum mechanics only by violating a fundamental conservation law"The perfect correlations of entangled spin states are the result of the conservation of total electron spin zero. The fall-off in correlations when Alice and Bob measure at angles different by Ψ (cos2Ψ) is a consequence of the "law of Malus."
Popescu-Rohrlich Boxes
In classic Bell experiments, Alice and Bob make a series of measurements with outcomes that can be described with binary numbers, (1,0) = | + >|- >, (0,1) = | - >| + >, (1,1) = | +>| + >, (0,0) = | - >| - >. They count the numbers of different outcomes and relate them to the probabilities of those outcomes, P(a,b|x,y), where x,y = ±1.
In the jargon of quantum nonlocality, P(a,b|x,y) is called a "box," because the correlation probabilities might be built into a physical box with inputs x,y = ±1 and outputs a,b = ±1. Compare David Mermin's devices.
a + b = x·y
where the addition operation + is modulo 2.
Decoherence and Disentanglement?
Might decoherence by environmental interactions cause the superposition of states | + - > - | - + > (equation 3) to collapse into one of these states and then into a product of single particle states, as Schrödinger told Einstein would happen for disentanglement? And does this also lead to the appearance of nonlocal simultaneous events, events that conserve angular momentum, in spatial regions where no-signaling applies? If so, conservation of angular momentum is all that is necessary for perfectly correlated quantum key distribution via entangled Bell states, without any "spooky action-at-a-distance," without any "influence" of one particle on the other at faster-than light speeds, just as Schrödinger thought in 1936. Alice's "first" measurement of a spin x-component would still be the "cause" of Bob's perfect correlation (assuming Bob measures in the same x-direction, of course). Correlations would be because the two spins were in a superposition of perfectly opposed directions before Alice's measurement, both conserving angular momentum. (Unnikrishnan, 2005) According to Asher Peres (1998), Nathan Rosen in 1931 described the normal hydrogen molecule with a two-particle wave function that he years later recognized was a Schrödinger "entangled state." Rosen wrote
ψ = ψ(al)ψ(b2) + ψ(b1)ψ(a2).
Can Perfect Correlations Be Explained by Conservation Laws?
David Bohm, Eugene Wigner, and even John Bell suggested that conservation of angular momentum (or particle spin) tells us that if one spin-1/2 electron is measured up, the other must be down. Albert Einstein used conservation of linear momentum in his development of the EPR Paradox. Bohm changed from the continuous variables position and momentum to the discrete quantum variable of electron spin.
Bohm wrote in his 1952 book Quantum Theory, "We shall now describe the hypothetical experiment of Einstein, Rosen, and Podolsky. We have modified the experiment somewhat, but the form is conceptually equivalent to that suggested by them, and considerably easier to treat mathematically."
The system containing the spin of two atoms has four basic wave functions, from which an arbitrary wave function can be constructed. [Because the wave function] has definite phase relations between ψc and ψd, the system must cover the states corresponding to ψc and ψd simultaneously. Thus, for a given atom, no component of the spin of a given variable exists with a precisely defined value, until interaction with a suitable system, such as a measuring apparatus, has taken place. But as soon as either atom (say, No. 1) interacts with an apparatus measuring a given component of the spin, definite phase relations between ψc and ψd are destroyed. This means that the system then acts as if it is either in the state ψc or ψd. Thus, in every instance in which particle No. 1 develops a definite spin component in, for example, the z direction, the wave function of particle No. 2 will automatically take such a form that it guarantees the development of the opposite value of σz if this particle also interacts with an apparatus which measures the same component of the spin. The wave function therefore describes the propagation of correlated potentialities. Because the expansion of the wave function ψ0 takes the same form when expanded in terms of the eigenfunctions of an arbitrary component of the spin, we conclude that similar correlations will be obtained if the same component of the spin of each atom in any direction is measured. Moreover, because the potentialities for development of a definite spin component are not realized irrevocably until interaction with the apparatus actually takes place, there is no inconsistency in the statement that while the atoms are still in flight, one can rotate the apparatus into an arbitrary direction, and thus choose to develop definite and correlated values for any desired spin component of each atom.Bohm explained that in classical theory, the spin correlations are produced because when the atoms of the original molecule separated, each atom would continue to have every component of its spin angular momentum opposite to that of the other. He says this is conservation of the spin-angular-momentum for each component of the separate vectors. In quantum mechanics, however, the investigator can measure either the x, y, or z component of the spin of a particle, but not more than one of these components, in any one experiment. Nevertheless, it still turns out that whichever component of particle 1 is measured, the results are correlated, so that if the same component of particle 2 is measured, it will always turn out to have the opposite value. He writes Now, if the spin were a classical angular momentum variable, the interpretation of this process would be as follows: While the two atoms were together in the form of a molecule, each component of the angular momentum of each atom would have a definite value that was always opposite to that of the other, thus making the total angular momentum equal to zero. When the atoms separated, each atom would continue to have every component of its spin angular momentum opposite to that of the other. The two spin-angular-momentum vectors would therefore be correlated. These correlations were originally produced when the atoms interacted in such a way as to form a molecule of zero total spin, but after the atoms separate, the correlations are maintained by the deterministic equations of motion of each spin vector separately, which bring about conservation of each component of the separate spin-angular- momentum vectors. Suppose now that one measures the spin angular momentum of any one of the particles, say No. 1. Because of the existence of correlations, one can immediately conclude that the angular-momentum vector of the other particle (No. 2) is equal and opposite to that of No. 1. In this way, one can measure the angular momentum of particle No. 2 indirectly by measuring the corresponding vector of particle No. 1. Let us now consider how this experiment is to be described in the quantum theory. Here, the investigator can measure either the x, y, or z component of the spin of particle No. 1, but not more than one of these components, in any one experiment. Nevertheless, it still turns out as we shall see that whichever component is measured, the results are correlated, so that if the same component of the spin of atom No. 2 is measured, it will always turn out to have the opposite value. This means that a measurement of any component of the spin of atom No. 1 provides, as in classical theory, an indirect measurement of the same component of the spin of atom No. 2. Since, by hypothesis, the two particles no longer interact, we have obtained a way of measuring an arbitrary component of the spin of particle No. 2 without in any way disturbing that particle.With his colleague, Yakir Aharonov, in 1957 Bohm reiterated his model We consider a molecule of total spin zero consisting of two atoms, each of spin one-half. The wave function of the system is thereforeEugene Wigner wrote in 1962
Writing a few years after Bohm, and one year before Bell, Wigner explicitly describes Einstein's work with the conservation of linear momentum as well as Bohm's conservation of angular momentum (spin) that explains perfect correlations between angular momentum (spin) components measured in the same direction
If a measurement of the momentum of one of the particles is carried out — the possibility of this is never questioned — and gives the result p, the state vector of the other particle suddenly becomes a (slightly damped) plane wave with the momentum -p. This statement is synonymous with the statement that a measurement of the momentum of the second particle would give the result -p, as follows from the conservation law for linear momentum. The same conclusion can be arrived at also by a formal calculation of the possible results of a joint measurement of the momenta of the two particles. One can go even further: instead of measuring the linear momentum of one particle, one can measure its angular momentum about a fixed axis. If this measurement yields the value mℏ, the state vector of the other particle suddenly becomes a cylindrical wave for which the same component of the angular momentum is -mℏ. This statement is again synonymous with the statement that a measurement of the said component of the angular momentum of the second particle certainly would give the value -mℏ. This can be inferred again from the conservation law of the angular momentum (which is zero for the two particles together) or by means of a formal analysis.John Bell wrote in 1964, With the example advocated by Bohm and Aharonov, the EPR argument is the following. Consider a pair of spin one-half particles formed somehow in the singlet spin state and moving freely in opposite directions. Measurements can be made, say by Stern-Gerlach magnets, on selected components of the spins σ1 and σ2. If measurement of the component σ1 • a, where a is some unit vector, yields the value + 1 then, according to quantum mechanics, measurement of σ2 • a must yield the value — 1 and vice versa. Now we make the hypothesis, and it seems one at least worth considering, that if the two measurements are made at places remote from one another the orientation of one magnet does not influence the result obtained with the other.Where Bohm and Wigner are explicit, Bell is implicitly using the conservation of total spin. Albert Einstein made the same implicit argument in 1933, shortly before EPR, though again with conservation of linear momentum, asking Leon Rosenfeld, Suppose two particles are set in motion towards each other with the same, very large, momentum, and they interact with each other for a very short time when they pass at known positions. Consider now an observer who gets hold of one of the particles, far away from the region of interaction, and measures its momentum: then, from the conditions of the experiment, he will obviously be able to deduce the momentum of the other particle. If, however, he chooses to measure the position of the first particle, he will be able tell where the other particle is.Supporters of the Copenhagen Interpretation claim that the properties of the particles (like angular or linear momentum) do not exist until they are measured. It was Pascual Jordan who claimed the measurement creates the value of a property. This is true when the preparation of the state is in an unknown linear combination (superposition) of quantum states. In our case, the entangled particles have been prepared in a superposition of [Bell] states, both of which have total spin zero.
ψ12 = (1/√2) [ ψ+ (1) ψ- (2) - ψ- (1) ψ+ (2)]
So whichever of these two states is projected by a later measurement or decoherence, it will put the two particles in opposite spin states, randomly + - or - + , but still supporting the views of Bohm, Wigner, and Bell, that they will be perfectly (anti-)correlated when measured, because of conservation of angular momentum (spin).
Einstein famously maintained that the strongest theories are those built on universal principles. Surely conservation principles, which Emmy Noether showed are built on the still deeper and simpler concept of symmetry, should be a part of any basis for physics, classical or quantum.
Conclusion
As Emmy Noether showed, conservation laws arise from deeper principles of symmetry.
The perfect symmetry between the indistinguishable electrons in Bohm's entanglement experiment, the perfect symmetry of their two-particle wave function, and the change of sign of that wave function under exchange of the two identical particles, all are evidence of synchronous events that are not directional "influences" of one on the other (not Einstein's "spooky action-at-a-distance").
They are simultaneous events in a "special frame" in which their center of mass is static. These events conserve the rotationally symmetric total spin zero at the same moment the two particles are disentangled and can no longer be described with a two-particle wave function.
They are now described by the product of two single-particle wave functions. The original pure state superposition has decohered. They are now disentangled and in a mixed state. As Schrödinger wrote, "knowledge of the phase relations between the complex constants ak has been entirely lost in consequence of the process of separation."
The symmetry and angular momentum conservation of entangled particles is theoretically deeper than classical and quantum physics.
The theory of entanglement is confirmed by all experiments that measure spins in exactly the same direction, as Bohm, Bell, and Wigner all agree. Unlike most quantum experiments, the results are not a statistical distribution around some expectation value. Conservation is deeper than quantum mechanics.
This entanglement is the basis for generation of random bit sequences at distant locations, which when compared are perfectly (anti-)correlated and usable as distributed quantum keys for securely encrypted communications.
It is also the basis for the instantaneous "teleportation" of quantum information.
Conservation is not a causal "force" by which one particle "acts" on the other, as Einstein feared. But it can explain the strange connection between widely separated events that he saw as "nonlocality," perhaps as early as 1905, explicitly described at the Solvay conference in 1927, and made famous in his 1935 EPR paper.
References
Alcock, J., Brunner, N., Pawlowski, M., and Scarani, V. (2009) "Recovering part of the quantum boundary from information causality," arxiv.org/0906.3464
Bell, J., (1964) "On the Einstein Podolsky Rosen Paradox." Physics 1.3 195. aps.org
Bub, J., (2004) "Why the Quantum?" Stud. Hist. Philos. Modern Phys. 35B, 241-266. arxiv.org/0402149
________, (2012) "Why the Tsirelson bound?," in Probability in Physics. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 167-185. arxiv.org/1208.3744
________, (2016) Bananaworld: Quantum Mechanics for Primates. Oxford University Press.
________, (2018) Totally Random: why nobody understands quantum mechanics (a serious comic on entanglement).. Princeton University Press.
Gisin, N., (2014) Quantum Chance: Nonlocality, Teleportation, and other Quantum Marvels, Springer.
Mermin, D. (1985) "Is the moon there
when nobody looks? Reality and the quantum theory," Physics Today 38.4 38-47 informationphilosopher.com
Pawłowski, M., Paterek, T., Kaszlikowski, D., Scarani, V., Winter, A., & Żukowski, M. (2009) "Information causality as a physical principle." Nature, 461(7267), 1101-1104. arxiv.org/0905.2292
Peres, Asher. (1998) "Quantum disentanglement and computation." Superlattices and Microstructures 23.3-4, 373-379. arxiv.org/9707047
Popescu, S., and Rohrlich, D. (1994) "Quantum nonlocality as an axiom." Foundations of Physics 24.3, 379-385. informationphilosopher.com
Rosen, N. (1931) "The normal state of the hydrogen molecule." Physical Review 38.12 2099. informationphilosopher.com
Schrödinger, E. (1936) "Probability Relations between Separated Systems," Proceedings of the Cambridge Physical Society 32, issue 2, p.446-452 informationphilosopher.com
Stuckey, W, Silberstein, M, McDevitt, T. and Kohler, I. (2019) "Why the Tsirelson bound? Bub’s question and Fuchs’ desideratum." Entropy 21.7, 692. mdpi.com
Stuckey, W, Silberstein, M, McDevitt, T. and Le, T.D. (2020) "Answering Mermin’s Challenge with Conservation per No Preferred Reference Frame." researchgate.net
Tsirelson, B.S. (1980) "Quantum Generalizations of Bell's Inequality." Lett. Math. Phys. 4, 93-100, informationphilosopher.com
Unnikrishnan, C.S. (2005) "Correlation functions. Bell's inequalities and the fundamental conservation laws." Europhys. Lett. 69, 489-495. arxiv.org/0407041
Normal | Teacher | Scholar
|