|
Topics
Introduction
Problems Freedom Knowledge Mind Life Chance Quantum Entanglement Scandals Philosophers Mortimer Adler Rogers Albritton Alexander of Aphrodisias Samuel Alexander William Alston Anaximander G.E.M.Anscombe Anselm Louise Antony Thomas Aquinas Aristotle David Armstrong Harald Atmanspacher Robert Audi Augustine J.L.Austin A.J.Ayer Alexander Bain Mark Balaguer Jeffrey Barrett William Barrett William Belsham Henri Bergson George Berkeley Isaiah Berlin Richard J. Bernstein Bernard Berofsky Robert Bishop Max Black Susan Blackmore Susanne Bobzien Emil du Bois-Reymond Hilary Bok Laurence BonJour George Boole Émile Boutroux Daniel Boyd F.H.Bradley C.D.Broad Michael Burke Jeremy Butterfield Lawrence Cahoone C.A.Campbell Joseph Keim Campbell Rudolf Carnap Carneades Nancy Cartwright Gregg Caruso Ernst Cassirer David Chalmers Roderick Chisholm Chrysippus Cicero Tom Clark Randolph Clarke Samuel Clarke Anthony Collins August Compte Antonella Corradini Diodorus Cronus Jonathan Dancy Donald Davidson Mario De Caro Democritus William Dembski Brendan Dempsey Daniel Dennett Jacques Derrida René Descartes Richard Double Fred Dretske Curt Ducasse John Earman Laura Waddell Ekstrom Epictetus Epicurus Austin Farrer Herbert Feigl Arthur Fine John Martin Fischer Frederic Fitch Owen Flanagan Luciano Floridi Philippa Foot Alfred Fouilleé Harry Frankfurt Richard L. Franklin Bas van Fraassen Michael Frede Gottlob Frege Peter Geach Edmund Gettier Carl Ginet Alvin Goldman Gorgias Nicholas St. John Green Niels Henrik Gregersen H.Paul Grice Ian Hacking Ishtiyaque Haji Stuart Hampshire W.F.R.Hardie Sam Harris William Hasker R.M.Hare Georg W.F. Hegel Martin Heidegger Heraclitus R.E.Hobart Thomas Hobbes David Hodgson Shadsworth Hodgson Baron d'Holbach Ted Honderich Pamela Huby David Hume Ferenc Huoranszki Frank Jackson William James Lord Kames Robert Kane Immanuel Kant Tomis Kapitan Walter Kaufmann Jaegwon Kim William King Hilary Kornblith Christine Korsgaard Saul Kripke Thomas Kuhn Andrea Lavazza James Ladyman Christoph Lehner Keith Lehrer Gottfried Leibniz Jules Lequyer Leucippus Michael Levin Joseph Levine George Henry Lewes C.I.Lewis David Lewis Peter Lipton C. Lloyd Morgan John Locke Michael Lockwood Arthur O. Lovejoy E. Jonathan Lowe John R. Lucas Lucretius Alasdair MacIntyre Ruth Barcan Marcus Tim Maudlin James Martineau Nicholas Maxwell Storrs McCall Hugh McCann Colin McGinn Michael McKenna Brian McLaughlin John McTaggart Paul E. Meehl Uwe Meixner Alfred Mele Trenton Merricks John Stuart Mill Dickinson Miller G.E.Moore Ernest Nagel Thomas Nagel Otto Neurath Friedrich Nietzsche John Norton P.H.Nowell-Smith Robert Nozick William of Ockham Timothy O'Connor Parmenides David F. Pears Charles Sanders Peirce Derk Pereboom Steven Pinker U.T.Place Plato Karl Popper Porphyry Huw Price H.A.Prichard Protagoras Hilary Putnam Willard van Orman Quine Frank Ramsey Ayn Rand Michael Rea Thomas Reid Charles Renouvier Nicholas Rescher C.W.Rietdijk Richard Rorty Josiah Royce Bertrand Russell Paul Russell Gilbert Ryle Jean-Paul Sartre Kenneth Sayre T.M.Scanlon Moritz Schlick John Duns Scotus Albert Schweitzer Arthur Schopenhauer John Searle Wilfrid Sellars David Shiang Alan Sidelle Ted Sider Henry Sidgwick Walter Sinnott-Armstrong Peter Slezak J.J.C.Smart Saul Smilansky Michael Smith Baruch Spinoza L. Susan Stebbing Isabelle Stengers George F. Stout Galen Strawson Peter Strawson Eleonore Stump Francisco Suárez Richard Taylor Kevin Timpe Mark Twain Peter Unger Peter van Inwagen Manuel Vargas John Venn Kadri Vihvelin Voltaire G.H. von Wright David Foster Wallace R. Jay Wallace W.G.Ward Ted Warfield Roy Weatherford C.F. von Weizsäcker William Whewell Alfred North Whitehead David Widerker David Wiggins Bernard Williams Timothy Williamson Ludwig Wittgenstein Susan Wolf Xenophon Scientists David Albert Philip W. Anderson Michael Arbib Bobby Azarian Walter Baade Bernard Baars Jeffrey Bada Leslie Ballentine Marcello Barbieri Jacob Barandes Julian Barbour Horace Barlow Gregory Bateson Jakob Bekenstein John S. Bell Mara Beller Charles Bennett Ludwig von Bertalanffy Susan Blackmore Margaret Boden David Bohm Niels Bohr Ludwig Boltzmann John Tyler Bonner Emile Borel Max Born Satyendra Nath Bose Walther Bothe Jean Bricmont Hans Briegel Leon Brillouin Daniel Brooks Stephen Brush Henry Thomas Buckle S. H. Burbury Melvin Calvin William Calvin Donald Campbell John O. Campbell Sadi Carnot Sean B. Carroll Anthony Cashmore Eric Chaisson Gregory Chaitin Jean-Pierre Changeux Rudolf Clausius Arthur Holly Compton John Conway Simon Conway-Morris Peter Corning George Cowan Jerry Coyne John Cramer Francis Crick E. P. Culverwell Antonio Damasio Olivier Darrigol Charles Darwin Paul Davies Richard Dawkins Terrence Deacon Lüder Deecke Richard Dedekind Louis de Broglie Stanislas Dehaene Max Delbrück Abraham de Moivre David Depew Bernard d'Espagnat Paul Dirac Theodosius Dobzhansky Hans Driesch John Dupré John Eccles Arthur Stanley Eddington Gerald Edelman Paul Ehrenfest Manfred Eigen Albert Einstein George F. R. Ellis Walter Elsasser Hugh Everett, III Franz Exner Richard Feynman R. A. Fisher David Foster Joseph Fourier George Fox Philipp Frank Steven Frautschi Edward Fredkin Augustin-Jean Fresnel Karl Friston Benjamin Gal-Or Howard Gardner Lila Gatlin Michael Gazzaniga Nicholas Georgescu-Roegen GianCarlo Ghirardi J. Willard Gibbs James J. Gibson Nicolas Gisin Paul Glimcher Thomas Gold A. O. Gomes Brian Goodwin Julian Gough Joshua Greene Dirk ter Haar Jacques Hadamard Mark Hadley Ernst Haeckel Patrick Haggard J. B. S. Haldane Stuart Hameroff Augustin Hamon Sam Harris Ralph Hartley Hyman Hartman Jeff Hawkins John-Dylan Haynes Donald Hebb Martin Heisenberg Werner Heisenberg Hermann von Helmholtz Grete Hermann John Herschel Francis Heylighen Basil Hiley Art Hobson Jesper Hoffmeyer John Holland Don Howard John H. Jackson Ray Jackendoff Roman Jakobson E. T. Jaynes William Stanley Jevons Pascual Jordan Eric Kandel Ruth E. Kastner Stuart Kauffman Martin J. Klein William R. Klemm Christof Koch Simon Kochen Hans Kornhuber Stephen Kosslyn Daniel Koshland Ladislav Kovàč Leopold Kronecker Bernd-Olaf Küppers Rolf Landauer Alfred Landé Pierre-Simon Laplace Karl Lashley David Layzer Joseph LeDoux Gerald Lettvin Michael Levin Gilbert Lewis Benjamin Libet David Lindley Seth Lloyd Werner Loewenstein Hendrik Lorentz Josef Loschmidt Alfred Lotka Ernst Mach Donald MacKay Henry Margenau Lynn Margulis Owen Maroney David Marr Humberto Maturana James Clerk Maxwell John Maynard Smith Ernst Mayr John McCarthy Barbara McClintock Warren McCulloch N. David Mermin George Miller Stanley Miller Ulrich Mohrhoff Jacques Monod Vernon Mountcastle Gerd B. Müller Emmy Noether Denis Noble Donald Norman Travis Norsen Howard T. Odum Alexander Oparin Abraham Pais Howard Pattee Wolfgang Pauli Massimo Pauri Wilder Penfield Roger Penrose Massimo Pigliucci Steven Pinker Colin Pittendrigh Walter Pitts Max Planck Susan Pockett Henri Poincaré Michael Polanyi Daniel Pollen Ilya Prigogine Hans Primas Giulio Prisco Zenon Pylyshyn Henry Quastler Adolphe Quételet Pasco Rakic Nicolas Rashevsky Lord Rayleigh Frederick Reif Jürgen Renn Giacomo Rizzolati A.A. Roback Emil Roduner Juan Roederer Robert Rosen Frank Rosenblatt Jerome Rothstein David Ruelle David Rumelhart Michael Ruse Stanley Salthe Robert Sapolsky Tilman Sauer Ferdinand de Saussure Jürgen Schmidhuber Erwin Schrödinger Aaron Schurger Sebastian Seung Thomas Sebeok Franco Selleri Claude Shannon James A. Shapiro Charles Sherrington Abner Shimony Herbert Simon Dean Keith Simonton Edmund Sinnott B. F. Skinner Lee Smolin Ray Solomonoff Herbert Spencer Roger Sperry John Stachel Kenneth Stanley Henry Stapp Ian Stewart Tom Stonier Antoine Suarez Leonard Susskind Leo Szilard Max Tegmark Teilhard de Chardin Libb Thims William Thomson (Kelvin) Richard Tolman Giulio Tononi Peter Tse Alan Turing Robert Ulanowicz C. S. Unnikrishnan Nico van Kampen Francisco Varela Vlatko Vedral Vladimir Vernadsky Clément Vidal Mikhail Volkenstein Heinz von Foerster Richard von Mises John von Neumann Jakob von Uexküll C. H. Waddington Sara Imari Walker James D. Watson John B. Watson Daniel Wegner Steven Weinberg August Weismann Paul A. Weiss Herman Weyl John Wheeler Jeffrey Wicken Wilhelm Wien Norbert Wiener Eugene Wigner E. O. Wiley E. O. Wilson Günther Witzany Carl Woese Stephen Wolfram H. Dieter Zeh Semir Zeki Ernst Zermelo Wojciech Zurek Konrad Zuse Fritz Zwicky Presentations ABCD Harvard (ppt) Biosemiotics Free Will Mental Causation James Symposium CCS25 Talk Evo Devo September 12 Evo Devo October 2 Evo Devo Goodness Evo Devo Davies Nov12 |
Dirac Three Polarizers Experiment
In his 1930 textbook The Principles of Quantum Mechanics, Paul Dirac introduced the uniquely quantum concepts of superposition and indeterminacy using polarized photons.
Dirac's examples suggest a very simple and inexpensive experiment to demonstrate
the notions of quantum states, the representation of a given state vector in another basis set of vectors, the preparation of quantum systems in states with known properties, and the measurement of various properties.
Measuring a system again after preparing it
Any measuring apparatus is also a state preparation system. We know that after a measurement of a photon which has shown it to be in a state of vertical polarization, for example, a second measurement with the same (vertical polarization detecting) capability will show the photon to be in the same state with probability unity. Quantum mechanics is not always uncertain. There is also no uncertainty if we measure the vertically polarized photon with a horizontal polarization detector. There is zero probability of the vertically polarized photon passing through a horizontal polarizer. It is completely absorbed.
Since any measurement increases the amount of information, there must be a compensating increase in entropy absorbed by or radiated away from the measuring apparatus. This is the Ludwig-Landauer Principle.
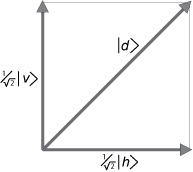
The natural basis set of vectors is usually one whose eigenvalues are the observables of our measurement system. In Dirac's bra and ket notation, the orthogonal basis vectors in our example are | v >, the photon in a vertically polarized state, and | h >, the photon in a horizontally polarized state. These two states are eigenstates of our measuring apparatus.
The interesting case to consider is a third measuring apparatus that prepares a photon in a diagonally polarized state 45° between | v > and | h >.
Dirac tells us this diagonally polarized photon can be represented as a superposition of vertical and horizontal states, with complex number coefficients that represent "probability amplitudes."
Thus,
in a known state is a Pauli measurement of the first kind
| d > = ( 1/√2) | v > + ( 1/√2) | h > (1)
Note that vector lengths are normalized to unity, and the sum of the squares of the probability amplitudes is also unity. This is the orthonormality condition needed to interpret the (squares of the) wave functions as probabilities, as first proposed by Max Born in 1927.
When these complex number coefficients are squared (actually when they are multiplied by their complex conjugates to produce positive real numbers), the numbers represent the probabilities of finding the photon in one or the other state, should a measurement be made. Dirac's bra vector is the complex conjugate of the corresponding ket vector.
It is these probability amplitudes that interfere in the two-slit experiment. To get the probabilities of finding a photon, we must square the probability amplitudes. Actually we must calculate the expectation value of some operator that represents an observable. The probability P of finding the photon in state |ψ> at location (in configuration space) r is
P(r) = < ψ | r | ψ >
No single experiment can convey all the wonder and non-intuitive character of quantum mechanics. But we believe Dirac's simple examples of polarized photons can teach us a lot. He thought that his simple examples provided a good introduction to the subject and we agree.
The Three Polarizers
We use three squares of polarizing sheet material to illustrate Dirac's explanation of quantum superposition of states and the collapse of a mixture of states to a pure state upon measurement or state preparation.
Here are the three polarizing sheets. They are a neutral gray color because they lose half of the light coming though them. The lost light is absorbed by the polarizer, converted to heat, and this accounts for the (Boltzmann) entropy gain required by our new information (Shannon entropy) about the exact polarization state of the transmitted photons.
The Wonder and Mystery of the Oblique Polarizer
As you would expect, any quantum mechanics experiment must contain an element of “Wow, that’s impossible!” or we are not getting to the non-intuitive and unique difference between quantum mechanics and the everyday classical mechanics. So let’s look at the amazing aspect of what Dirac is getting to, and then we will see how quantum mechanics explains it.
We turn the third polarizer C so its polarization is along the diagonal. Dirac tells us that the wave function of light passing through this polarizer can be regarded as in a mixed state, a superposition of vertical and horizontal states. As Einstein agreed, the information as to the exact state in which the photon will be found following a measurement does not exist.
We can make a measurement that detects vertically polarized photons by holding up the vertical polarizer A in front of the oblique polarizer C. Either a photon comes through A or it does not. Similarly, we can hold up the horizontal polarizer B in front of C. If we see a photon, it is horizontally polarized.
From equation (1) we see that the probability of detecting a photon diagonally polarized by C, if our measuring apparatus (polarizer B) is measuring for horizontally polarized photons, is 1/2. Similarly, if we were to measure for vertically polarized photons, we have the same 50% chance of detecting a photon.
Going back to polarizers A and B crossed at a 90° angle, we know that no light comes through when we cross the polarizers.
If we hold up polarizer C along the 45 degree diagonal and place it in front of (or behind) the cross polarizers, nothing changes. No light is getting through.
But here is the amazing, impossible part. If you insert polarizer C between A and B along a 45-degree diagonal, some light now gets through. Note that C is slipped between A (in the rear) and B (in front).
What is happening here quantum mechanically?
The Quantum Physics Explanation
Let’s start with the A polarizer in the back. It prepares the the photons in the vertical polarization state | v >. If we now had just polarizer B, it would measure for horizontal photons. None are coming through A, so no photons get through B.
When we interpose C at the oblique angle, it measures for diagonal photons. The vertically polarized photons coming through A can be considered in a superposition of states at a 45 degree angle and a -45 degree angle. Photons at -45 degrees are absorbed by C. Those at +45 degrees pass through C.
C makes a measurement of 45 degree photons. It can also be viewed as a preparation of 45 degree photons. Only half the photons come through polarizer C, but they have been prepared in a state of diagonal polarization | d >.
The original vertical photons coming through A had no chance of getting through B, but the diagonal photons passing through C (half the original photons) can now be regarded as in a linear superposition of vertical and horizontal photons, and the horizontal photons can now pass through B. Those vertically polarized will get absorbed by B, as usual.
Recall from equation (1) that | d > is a superposition of the basis vectors | v > and | h >, with coefficients 1/√2, which when squared give us probabilities 1/2. Fifty percent of these photons emerging from C will pass though B. One quarter or 25% of the original A photons make it through.
This happens if we send just one photon through at a time, just as with the two-slit experiment. Just as we can not say that the photon passes through a particular slit , we cannot know which state a particular polarized photon is in after passing through C. Statistically, it is in either horizontal or vertical polarization. When a measurement is made by polarizer B, one half of the 25% that came through C will pass though B, or one-eighth of the original light.
Dirac's Description of the Three Polarizers
In chapter 1 of his book The Principles of Quantum Mechanics, Paul Dirac describes the experiment. (complete text of Chapter 1)
from section 2, The Polarization of photons, pp.5-7 Suppose we have a beam of light passing through a [horizontal polarizer B], which has the property of letting through only light plane-polarized [horizontally]. Classical electrodynamics tells us what will happen for any given polarization of the incident beam. If this beam is [horizontally] polarized..., it will all go through the [polarizer]; if [vertically polarized], none of it will go through; while if polarized at an angle α, a fraction sin2α will go through. How are we to understand these results on a photon basis?Dirac describes the superposition of states with further comments on indeterminacy.
We animated Dirac's idea of introducing an oblique polarizer between the two crossed polarizers A and B that are blocking all light. Adding this filter actually allows more photons to pass through, which is counter-intuitive. 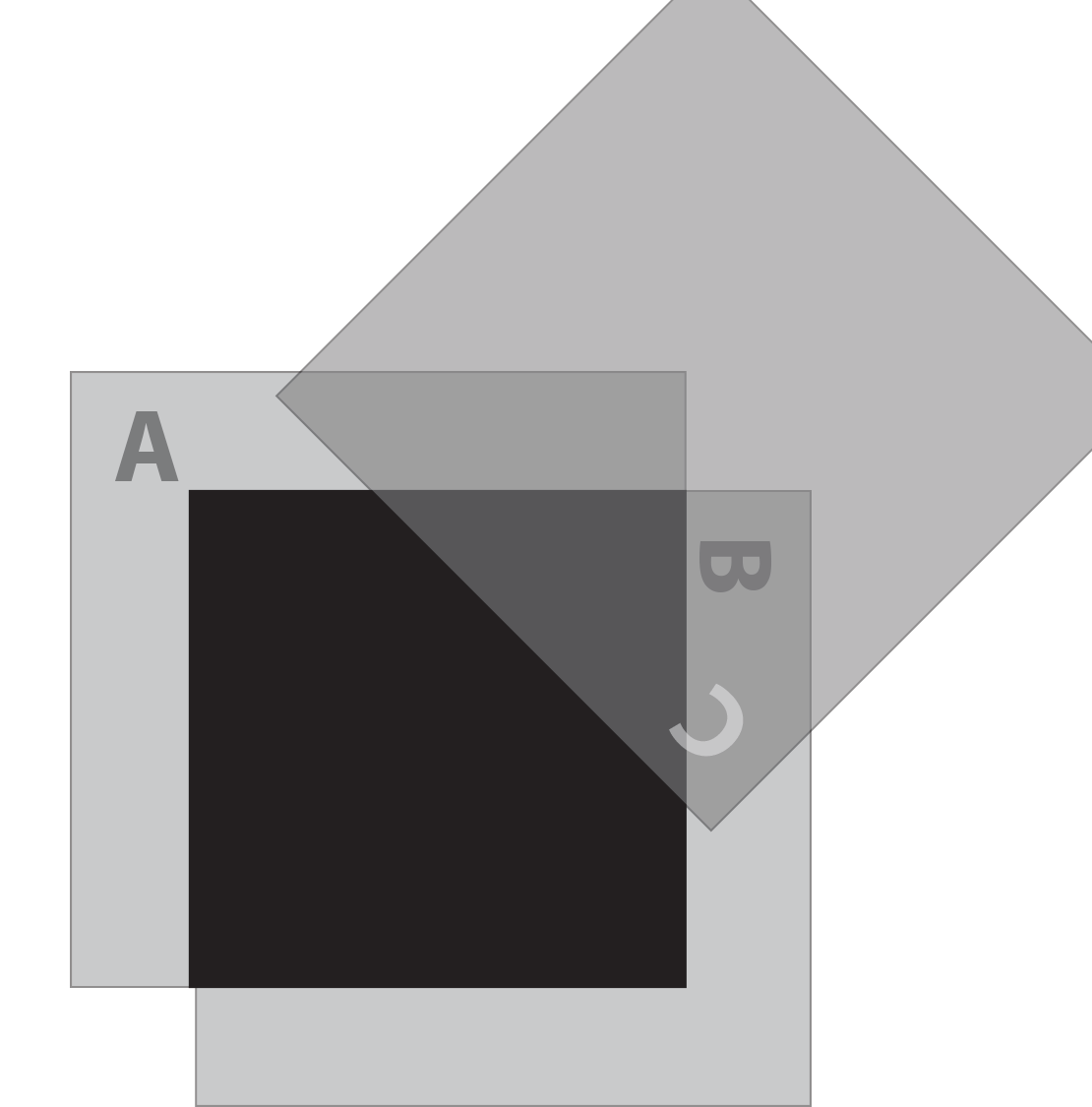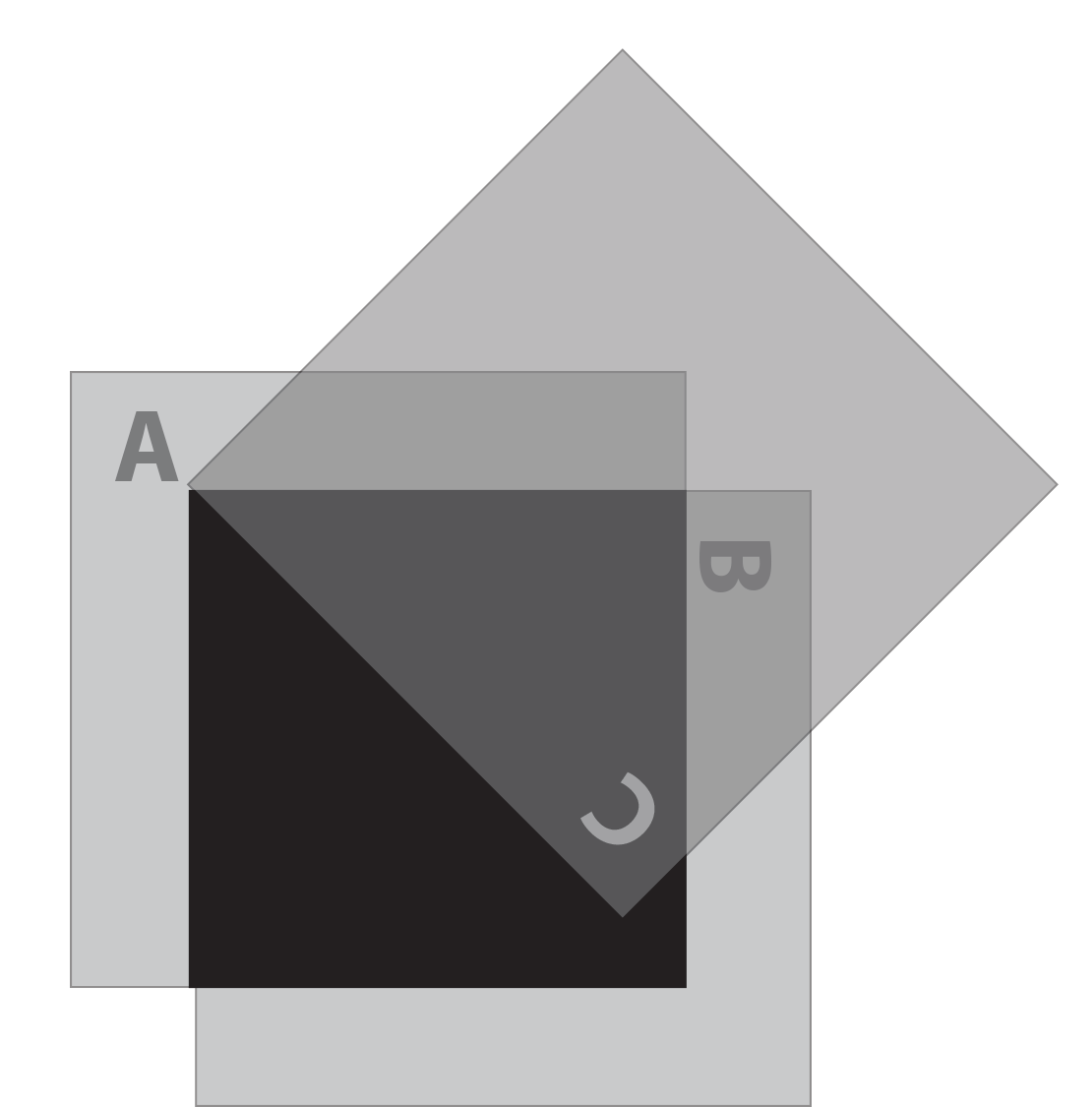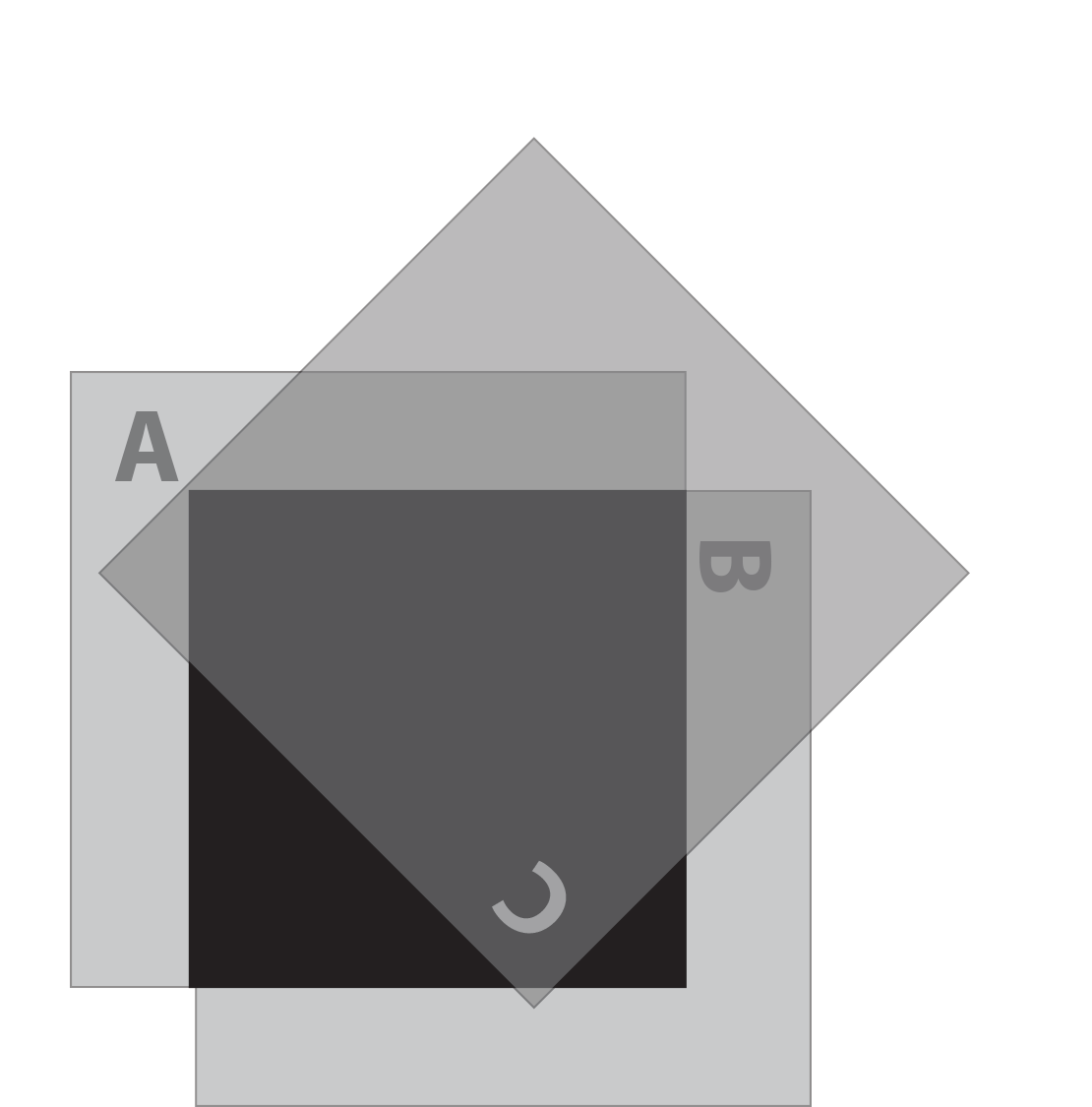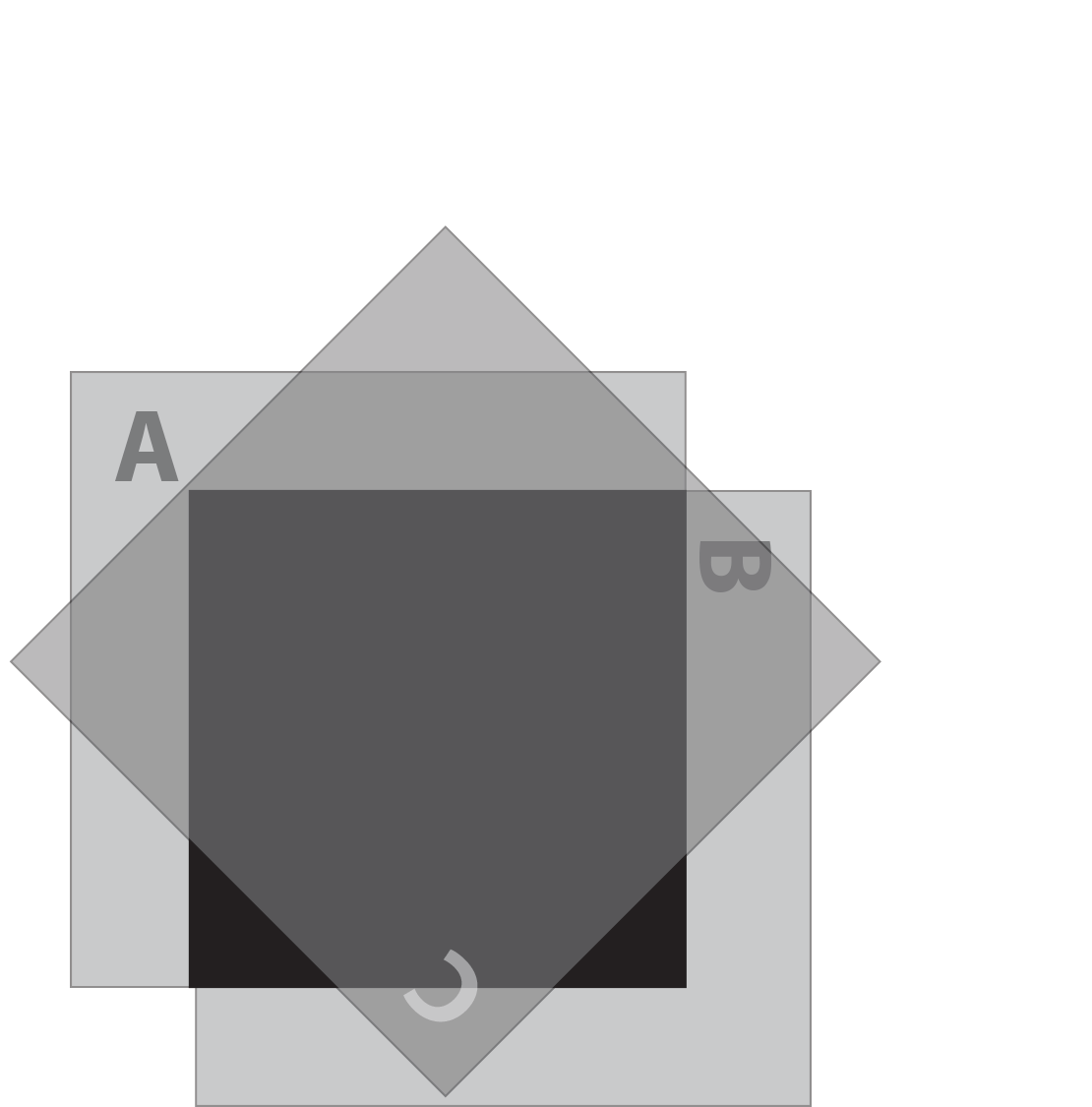 Normal | Teacher | Scholar
Normal | Teacher | Scholar
|
||||||||||||||||||||