|
Topics
Introduction
Problems Freedom Knowledge Mind Life Chance Quantum Entanglement Scandals Philosophers Mortimer Adler Rogers Albritton Alexander of Aphrodisias Samuel Alexander William Alston Anaximander G.E.M.Anscombe Anselm Louise Antony Thomas Aquinas Aristotle David Armstrong Harald Atmanspacher Robert Audi Augustine J.L.Austin A.J.Ayer Alexander Bain Mark Balaguer Jeffrey Barrett William Barrett William Belsham Henri Bergson George Berkeley Isaiah Berlin Richard J. Bernstein Bernard Berofsky Robert Bishop Max Black Susan Blackmore Susanne Bobzien Emil du Bois-Reymond Hilary Bok Laurence BonJour George Boole Émile Boutroux Daniel Boyd F.H.Bradley C.D.Broad Michael Burke Jeremy Butterfield Lawrence Cahoone C.A.Campbell Joseph Keim Campbell Rudolf Carnap Carneades Nancy Cartwright Gregg Caruso Ernst Cassirer David Chalmers Roderick Chisholm Chrysippus Cicero Tom Clark Randolph Clarke Samuel Clarke Anthony Collins August Compte Antonella Corradini Diodorus Cronus Jonathan Dancy Donald Davidson Mario De Caro Democritus William Dembski Brendan Dempsey Daniel Dennett Jacques Derrida René Descartes Richard Double Fred Dretske Curt Ducasse John Earman Laura Waddell Ekstrom Epictetus Epicurus Austin Farrer Herbert Feigl Arthur Fine John Martin Fischer Frederic Fitch Owen Flanagan Luciano Floridi Philippa Foot Alfred Fouilleé Harry Frankfurt Richard L. Franklin Bas van Fraassen Michael Frede Gottlob Frege Peter Geach Edmund Gettier Carl Ginet Alvin Goldman Gorgias Nicholas St. John Green Niels Henrik Gregersen H.Paul Grice Ian Hacking Ishtiyaque Haji Stuart Hampshire W.F.R.Hardie Sam Harris William Hasker R.M.Hare Georg W.F. Hegel Martin Heidegger Heraclitus R.E.Hobart Thomas Hobbes David Hodgson Shadsworth Hodgson Baron d'Holbach Ted Honderich Pamela Huby David Hume Ferenc Huoranszki Frank Jackson William James Lord Kames Robert Kane Immanuel Kant Tomis Kapitan Walter Kaufmann Jaegwon Kim William King Hilary Kornblith Christine Korsgaard Saul Kripke Thomas Kuhn Andrea Lavazza James Ladyman Christoph Lehner Keith Lehrer Gottfried Leibniz Jules Lequyer Leucippus Michael Levin Joseph Levine George Henry Lewes C.I.Lewis David Lewis Peter Lipton C. Lloyd Morgan John Locke Michael Lockwood Arthur O. Lovejoy E. Jonathan Lowe John R. Lucas Lucretius Alasdair MacIntyre Ruth Barcan Marcus Tim Maudlin James Martineau Nicholas Maxwell Storrs McCall Hugh McCann Colin McGinn Michael McKenna Brian McLaughlin John McTaggart Paul E. Meehl Uwe Meixner Alfred Mele Trenton Merricks John Stuart Mill Dickinson Miller G.E.Moore Ernest Nagel Thomas Nagel Otto Neurath Friedrich Nietzsche John Norton P.H.Nowell-Smith Robert Nozick William of Ockham Timothy O'Connor Parmenides David F. Pears Charles Sanders Peirce Derk Pereboom Steven Pinker U.T.Place Plato Karl Popper Porphyry Huw Price H.A.Prichard Protagoras Hilary Putnam Willard van Orman Quine Frank Ramsey Ayn Rand Michael Rea Thomas Reid Charles Renouvier Nicholas Rescher C.W.Rietdijk Richard Rorty Josiah Royce Bertrand Russell Paul Russell Gilbert Ryle Jean-Paul Sartre Kenneth Sayre T.M.Scanlon Moritz Schlick John Duns Scotus Albert Schweitzer Arthur Schopenhauer John Searle Wilfrid Sellars David Shiang Alan Sidelle Ted Sider Henry Sidgwick Walter Sinnott-Armstrong Peter Slezak J.J.C.Smart Saul Smilansky Michael Smith Baruch Spinoza L. Susan Stebbing Isabelle Stengers George F. Stout Galen Strawson Peter Strawson Eleonore Stump Francisco Suárez Richard Taylor Kevin Timpe Mark Twain Peter Unger Peter van Inwagen Manuel Vargas John Venn Kadri Vihvelin Voltaire G.H. von Wright David Foster Wallace R. Jay Wallace W.G.Ward Ted Warfield Roy Weatherford C.F. von Weizsäcker William Whewell Alfred North Whitehead David Widerker David Wiggins Bernard Williams Timothy Williamson Ludwig Wittgenstein Susan Wolf Xenophon Scientists David Albert Philip W. Anderson Michael Arbib Bobby Azarian Walter Baade Bernard Baars Jeffrey Bada Leslie Ballentine Marcello Barbieri Jacob Barandes Julian Barbour Horace Barlow Gregory Bateson John S. Bell Mara Beller Charles Bennett Ludwig von Bertalanffy Susan Blackmore Margaret Boden David Bohm Niels Bohr Ludwig Boltzmann John Tyler Bonner Emile Borel Max Born Satyendra Nath Bose Walther Bothe Jean Bricmont Hans Briegel Leon Brillouin Daniel Brooks Stephen Brush Henry Thomas Buckle S. H. Burbury Melvin Calvin William Calvin Donald Campbell John O. Campbell Sadi Carnot Sean B. Carroll Anthony Cashmore Eric Chaisson Gregory Chaitin Jean-Pierre Changeux Rudolf Clausius Arthur Holly Compton John Conway Simon Conway-Morris Peter Corning George Cowan Jerry Coyne John Cramer Francis Crick E. P. Culverwell Antonio Damasio Olivier Darrigol Charles Darwin Paul Davies Richard Dawkins Terrence Deacon Lüder Deecke Richard Dedekind Louis de Broglie Stanislas Dehaene Max Delbrück Abraham de Moivre David Depew Bernard d'Espagnat Paul Dirac Theodosius Dobzhansky Hans Driesch John Dupré John Eccles Arthur Stanley Eddington Gerald Edelman Paul Ehrenfest Manfred Eigen Albert Einstein George F. R. Ellis Walter Elsasser Hugh Everett, III Franz Exner Richard Feynman R. A. Fisher David Foster Joseph Fourier George Fox Philipp Frank Steven Frautschi Edward Fredkin Augustin-Jean Fresnel Karl Friston Benjamin Gal-Or Howard Gardner Lila Gatlin Michael Gazzaniga Nicholas Georgescu-Roegen GianCarlo Ghirardi J. Willard Gibbs James J. Gibson Nicolas Gisin Paul Glimcher Thomas Gold A. O. Gomes Brian Goodwin Julian Gough Joshua Greene Dirk ter Haar Jacques Hadamard Mark Hadley Ernst Haeckel Patrick Haggard J. B. S. Haldane Stuart Hameroff Augustin Hamon Sam Harris Ralph Hartley Hyman Hartman Jeff Hawkins John-Dylan Haynes Donald Hebb Martin Heisenberg Werner Heisenberg Hermann von Helmholtz Grete Hermann John Herschel Francis Heylighen Basil Hiley Art Hobson Jesper Hoffmeyer John Holland Don Howard John H. Jackson Ray Jackendoff Roman Jakobson E. T. Jaynes William Stanley Jevons Pascual Jordan Eric Kandel Ruth E. Kastner Stuart Kauffman Martin J. Klein William R. Klemm Christof Koch Simon Kochen Hans Kornhuber Stephen Kosslyn Daniel Koshland Ladislav Kovàč Leopold Kronecker Bernd-Olaf Küppers Rolf Landauer Alfred Landé Pierre-Simon Laplace Karl Lashley David Layzer Joseph LeDoux Gerald Lettvin Michael Levin Gilbert Lewis Benjamin Libet David Lindley Seth Lloyd Werner Loewenstein Hendrik Lorentz Josef Loschmidt Alfred Lotka Ernst Mach Donald MacKay Henry Margenau Lynn Margulis Owen Maroney David Marr Humberto Maturana James Clerk Maxwell John Maynard Smith Ernst Mayr John McCarthy Barbara McClintock Warren McCulloch N. David Mermin George Miller Stanley Miller Ulrich Mohrhoff Jacques Monod Vernon Mountcastle Gerd B. Müller Emmy Noether Denis Noble Donald Norman Travis Norsen Howard T. Odum Alexander Oparin Abraham Pais Howard Pattee Wolfgang Pauli Massimo Pauri Wilder Penfield Roger Penrose Massimo Pigliucci Steven Pinker Colin Pittendrigh Walter Pitts Max Planck Susan Pockett Henri Poincaré Michael Polanyi Daniel Pollen Ilya Prigogine Hans Primas Giulio Prisco Zenon Pylyshyn Henry Quastler Adolphe Quételet Pasco Rakic Nicolas Rashevsky Lord Rayleigh Frederick Reif Jürgen Renn Giacomo Rizzolati A.A. Roback Emil Roduner Juan Roederer Robert Rosen Frank Rosenblatt Jerome Rothstein David Ruelle David Rumelhart Michael Ruse Stanley Salthe Robert Sapolsky Tilman Sauer Ferdinand de Saussure Jürgen Schmidhuber Erwin Schrödinger Aaron Schurger Sebastian Seung Thomas Sebeok Franco Selleri Claude Shannon James A. Shapiro Charles Sherrington Abner Shimony Herbert Simon Dean Keith Simonton Edmund Sinnott B. F. Skinner Lee Smolin Ray Solomonoff Herbert Spencer Roger Sperry John Stachel Kenneth Stanley Henry Stapp Ian Stewart Tom Stonier Antoine Suarez Leonard Susskind Leo Szilard Max Tegmark Teilhard de Chardin Libb Thims William Thomson (Kelvin) Richard Tolman Giulio Tononi Peter Tse Alan Turing Robert Ulanowicz C. S. Unnikrishnan Nico van Kampen Francisco Varela Vlatko Vedral Vladimir Vernadsky Clément Vidal Mikhail Volkenstein Heinz von Foerster Richard von Mises John von Neumann Jakob von Uexküll C. H. Waddington Sara Imari Walker James D. Watson John B. Watson Daniel Wegner Steven Weinberg August Weismann Paul A. Weiss Herman Weyl John Wheeler Jeffrey Wicken Wilhelm Wien Norbert Wiener Eugene Wigner E. O. Wiley E. O. Wilson Günther Witzany Carl Woese Stephen Wolfram H. Dieter Zeh Semir Zeki Ernst Zermelo Wojciech Zurek Konrad Zuse Fritz Zwicky Presentations Biosemiotics Free Will Mental Causation James Symposium CCS25 Talk Evo Devo September 12 Evo Devo October 2 Evo Devo Goodness Evo Devo Davies Nov12 |
Alfred North Whitehead

Whitehead in a Nutshell
Before he came to Harvard, Whitehead wrote three important books while at Trinity College, Cambridge, that put forth his speculative theories on space, time, matter, and energy - An Enquiry Concerning the Principles of Natural Knowledge (PNK , 1919), The Concept of Nature (CN, 1920), and Principle of Relativity (PoR, 1922),
in PNK Whitehead calls the instantaneous and infinitesimal points of special relativity "event-particles." (p.33) He then says that the events of his theory will include large numbers of "event-particles" because his events are extended in both space and time, an idea he calls "extensive abstraction."(p.101) It is only these finite volumes of space and durations in time that can be perceived or apprehended by an observer. Whitehead is correct that perceivable happenings always involve relatively large numbers of material particles interacting over a period of time, especially biological events.
In CN Whitehead argues against what he calls the "bifurcation of nature" (p.24) that divides the world into the appearance of sense-data (the empiricist's secondary qualities) and the "reality" of the molecules and light energy that are the causes (or primary qualities). For Whitehead there is only one nature. He also argues against the notion of absolute space and time, claiming that the important information is the matter in space and the relative positions of bits of matter.
In PoR Whitehead develops a principle of relativity that differs in significant and erroneous ways from the special and general theories of Einstein's relativity, oddly claiming, for example, that "the ether is an observed character of things observed." (p.5) He developed explanations for shifts in spectroscopic line wavelengths (p.70) and for the splitting of lines that turn out not to have been correct.
Whitehead's "philosophy of organism" analyzes the perception of experience as a continuing series of discrete "events" that are created and destroyed. He goes beyond the simple materialist view of elementary particles interacting in space and time, merely following the laws of classical and quantum mechanics. Beyond the atomic particles and the electromagnetic and gravitational fields, and beyond the conservation laws for energy and momentum, Whitehead sees an "organic" evolutionary process of creation and valuation.
We need to understand what it is exactly that Whitehead thinks is being created and why it can serve as a basis for values. We will argue that Whitehead's process is "organic" because it explains evolution, not merely biological evolution but the cosmic evolution of the galaxies, stars, and planets as well as the creation of all matter from the primordial elementary particles.
In addition to his deep understanding of mathematics, Whitehead may have understood the development of modern physics better than any living philosopher in his day. He saw the greatest invention of the nineteenth century as the invention of the method of invention, namely the scientific method and newly created scientific information, but even more deeply, the means by which novel ideas of all kinds are created.
Whitehead identified four great novel ideas as the new nineteenth-century foundations of physical science, fields, particles, conservation principles, and evolution.
One of the ideas is that of a field of physical activity pervading all space, even where there is an apparent vacuum. This notion had occurred to many people, under many forms. We remember the medieval axiom, nature abhors a vacuum... Thus in the seventies of the last century, some main physical sciences were established on a basis which presupposed the idea of continuity.Although he starts with the latest science, Whitehead also builds on the ancient problem of the One and the Many, distinctions between the Parmenidean One/Being and the Heraclitean/Democritean flux/many/becoming. He describes the thinking of the mind as a succession of transitions in which many entities become a new unity, a one, after which the new unity/entity becomes part of a new many, etc., etc. He describes this as an organic process. By starting with the many, Whitehead reads the Platonic divided line from right to left.
The Sources of Whitehead's Ideas
Whitehead was an extraordinary mathematician who read widely in ancient and modern philosophy. He is said to have memorized many parts of the great Kantian critique and its architectonic of categories, which Whitehead emulated in Process and Reality. But Whitehead also took a great interest in the science of his times. His readings of relativity and quantum mechanics greatly influenced the creation of his philosophy and "theology," which is arguably free of any conventional notion of a God, but rather as a discovery of the process that produces reality, and thus fits many theists' definition of a god.
We can see now that Whitehead actually understood very little of these two pillars of modern physics. He misinterpreted both Albert Einstein's relativity and Niels Bohr's quantum theory. But we can identify two basic elements that he borrowed from them to ground his understanding of the nature of reality as a process.
From relativity he took the idea of an event in space and time. His British idealist colleague John McTaggart had formulated two ideas of time. Whitehead likely preferred McTaggart's A series, which is both the common sense view and the metaphysical view now known as presentism. McTaggart's B series is the notion that all times and thus all events, past, present, and future, are all existent and equally real. This is the view of special relativity.
Albert Einstein's four-dimensional space-time was called a "block universe" by Hermann Minkowski. In such a universe causal relations are explained by what Whitehead called "simple location" in space-time. Each event can be caused by something in its past "light cone" andin turn the event has a causal influence over events in its future "light cone.
This is the deterministic Laplacian universe in which a super-intelligence can know the complete past and the single possible future from knowledge of the positions and velocities of all the material particles at the one instant of the present. It was actually Gottfried Leibniz who saw this universe as a consequence of continuous differential equations using his calculus or Isaac Newton's fluxions. Whitehead rejected this reductive view as "scientific materialism."
From quantum mechanics Whitehead took the notion that nature is discontinuous and discrete from Bohr's "old quantum theory" with his "quantum jumps" between discrete energy levels. Perhaps under the influence of Henri Bergson's duration theory of time as discrete intervals, Whitehead analyzed an event, a moment in space-time, stretching it out to a duration or interval between a beginning and an end time, which he later called an "occasion."
From inside that interval, one can look back to perceive the many past events, any or all of which may contribute to this moment seen as a single event, a single cause that will affect many future, as yet unrealized, events.
Which of those past events are selected, and Whitehead's unique contribution is to see that a selection may combine together a large number of past events as causes, introduces an element of novelty and creation. Whitehead's "process" is very far from the simplistic idea of a single causal chain of event-cause-event-cause, etc. And as a temporal process, it is not the familiar Hegelian dialectic of thesis (idea) - antithesis (criticism) - synthesis (Aufhebung) spiraling upward to the ultimate Absolute Idea.
Borrowing from the language of the British empiricists John Locke, David Hume, and especially George Berkeley, Whitehead describes his process as subjective perceptions forming concepts about objects. He views the immediate present subject as perceiving the past events (now simply objects) and freely choosing some of them (he calls this prehending them) to be combined in new ways (he calls this concretion or concrescence - a growing together) to create a new idea or concept (he calls a creature), which immediately falls into the past light cone (he calls this perishing), becoming just one more object. Some of the past many have become a new one, which can join the future many, converging onto future events that will again each become one.
Whitehead's Philosophical Works
In his Lowell Lectures of 1925 (which became the classic book Science and the Modern World), Whitehead railed against "scientific materialism" and the deterministic claims of science. In his preface, he describes his goal,
The present book embodies a study of some aspects of Western culture during the past three centuries, in so far as it has been influenced by the development of science. This study has been guided by the conviction that the mentality of an epoch springs from the view of the world which is, in fact, dominant in the educated sections of the communities in question... Philosophy, in one of its functions, is the critic of cosmologies. It is its function to harmonise, re-fashion, and justify divergent intuitions as to the nature of things. It has to insist on the scrutiny of the ultimate ideas, and on the retention of the whole of the evidence in shaping our cosmological scheme. Its business is to render explicit, and—so far as may be—efficient, a process which otherwise is unconsciously performed without rational tests. Bearing this in mind, I have avoided the introduction of a variety of abstruse detail respecting scientific advance. What is wanted, and what I have striven after, is a sympathetic study of main ideas as seen from the inside. If my view of the function of philosophy is correct, it is the most effective of all the intellectual pursuits. It builds cathedrals before the workmen have moved a stone, and it destroys them before the elements have worn down their arches. It is the architect of the buildings of the spirit, and it is also their solvent: —and the spiritual precedes the material. Philosophy works slowly. Thoughts lie dormant for ages; and then, almost suddenly as it were, mankind finds that they have embodied themselves in institutions.Whitehead proceeds to build a new philosophy of the spirit and mind that bases nature on the concept of organism, and not upon the concept of matter. Like Plato (to whom Whitehead is perhaps the most famous footnote), Whitehead privileges form over content, the ideal over the material world. Although he claims to avoid the "abstruse detail" about science, he elaborates a complex and often obscure vocabulary of terms to describe the process of thought that creates the eternal ideas, based on the mind's perception of experiences. Whitehead's writing style is dense, with mesmerizing repetitive variations on his basic themes, like G.W.F.Hegel, whose philosophy Whitehead learned from the equally verbose British idealists F.H.Bradley and John McTaggart. Like the empiricist George Berkeley who denied the material world to stress the immaterial ideas that we create through our perceptions, Whitehead's philosophy of organism invents a dense language to describe and analyze the process of thinking. Where "esse est percipi," to be is to be perceived, was Berkeley's motto, we might say Whitehead believed that his dialectical analysis of the "process" of perception and conception will reveal the true reality as the sum of our experiences. For Whitehead and for Berkeley, the process of a subject perceiving objects and thinking with concepts is reality. Whitehead calls for a wider field of abstraction than that used in the scientific field of thought, we should have in our minds a more concrete (sic) analysis of our concepts, which will stand nearer to the "complete concreteness of our intuitive experience." Whitehead's notions of concrete, concretion, even his later concrescence may blur the usual mapping of the ideal/material dualism onto the abstract/concrete. Whitehead's call for wider "thinking about thinking" as an organic process extends "ideas" from the mind of God to the interactions of elementary particles as enduring "patterns" over time. He also introduces "eternal objects" (perhaps the Platonic Forms?) that are outside of time. Such an analysis should find itself a niche for the concepts of matter and spirit, as abstractions in terms of which much of our physical experience can be interpreted. It is in the search for this wider basis for scientific thought that Berkeley is so important. He launched his criticism shortly after the schools of Newton and Locke had completed their work, and laid his finger exactly on the weak spots which they had left. I do not propose to consider either the subjective idealism which has been derived from him, or the schools of development which trace their descent from Hume and Kant respectively. My point will be that—whatever the final metaphysics you may adopt—there is another line of development embedded in Berkeley, pointing to the analysis which we are in search of. Berkeley overlooked it, partly by reason of the over-intellectualism of philosophers, and partly by his haste to have recourse to an idealism with its objectivity grounded in the mind of God. You will remember that I have already stated that the key of the problem lies in the notion of simple location. Berkeley, in effect, criticises this notion.We are now boldfacing Whitehead's critical new terms. Whitehead quotes Francis Bacon's Natural History as claiming that "all bodies whatsoever, though they have no sense, yet they have perception". He then replaces standard terms like perception with variant terms that do not imply an ordinary sensing being. He italicizes the important terms, to say I construed perception (as used by Bacon) as meaning taking account of the essential character of the thing perceived, and I construed sense as meaning cognition. We certainly do take account of things of which at the time we have no explicit cognition. We can even have a cognitive memory of the taking account, without having had a contemporaneous cognition. Also, as Bacon points out by his statement,'. . . for else all bodies would be alike one to another,' it is evidently some element of the essential character which we take account of, namely something on which diversity is founded and not mere bare logical diversity. The word perceive is, in our common usage, shot through and through with the notion of cognitive apprehension. So is the word apprehension, even with the adjective cognitive omitted. I will use the word prehension for uncognitive apprehension: by this I mean apprehension which may or may not be cognitive. Now take Euphranor's last remark: 'Is it not plain, therefore, that neither the castle, the planet, nor the cloud, which you see here, are those real ones which you suppose exist at a distance?' Accordingly, there is a prehension, here in this place, of things which have a reference to other places. Now go back to Berkeley's sentences, quoted from his Principles of Human Knowledge. He contends that what constitutes the realisation of natural entities is the being perceived within the unity of mind. We can substitute the concept, that the realisation is a gathering of things into the unity of a prehension; and that what is thereby realised is the prehension, and not the things. This unity of a prehension defines itself as a here and a now, and the things so gathered into the grasped unity have essential reference to other places and other times. Here Whitehead has given us the first few elements of his philosophy of organism. The mind can "supply experiences other than those provided by the body." "Mental states enter into the plan of the total organism and thus modify the plans of the successive subordinate organisms until the ultimate smallest organisms, such as electrons, are reached." "Molecules may blindly run in accordance with the general laws, but the molecules differ in their intrinsic characters according to the general organic plans of the situations in which they find themselves." This is all well and good, except that Whitehead is wrong about electrons and other material particles. They have no internal plans and purposes of their own. We have bolded terms that will acquire very specific technical meanings for Whitehead in his next two works, especially in his magnum opus Process and Reality. A year later, in 1926 Whitehead gave a second set of Lowell Lectures, this time at King's Chapel in Boston. They were published as Religion in the Making. Whitehead's embrace of religion and his idea of God account for his continued success among a subset of philosophers and theologians. His work is a throwback to before the presocratics who stopped explaining physical processes as the work of gods. Recent editions of Religion in the Making have a technical glossary of terms, which is very helpful. The first two lectures include a brief history of religion, the major faiths and their dogmas. In lecture 3, "Body and Spirit," Whitehead builds on a few terms from Science and the Modern World, such as abstract, actual, event, experience, character, prehension, unification. He adds new terms, familiar words with new technical meanings, and several new terms - concretion, creature, creativity, entity, epochal, indetermination, realisation, occasion His magnum opus, Process and Reality, will again expand the Whitehead jargon, but much is here. See our draft of a Whitehead glossary below. In the second half of the book, Whitehead begins to speak with terminology that is at once familiar yet jarring in his apparent meaning. The Dean of the Divinity School of the University of Chicago remarked on his first reading, "It is infuriating, and I must say embarrassing as well, to read page after page of relatively familiar words without understanding a single sentence." There are many ways of analyzing the universe, conceived as that which is comprehensive of all that there is. In a description it is thus necessary to correlate these different routes of analysis. First, consider the analysis into (1) the actual world, passing in time; and (2) those elements which go to its formation. Such formative elements are not themselves actual and passing; they are the factors which are either non-actual or non-temporal, disclosed in the analysis of what is both actual and temporal. They constitute the formative character of the actual temporal world. We know nothing beyond this temporal world and the formative elements which jointly constitute its character. The temporal world and its formative elements constitute for us the all-inclusive universe. These formative elements are: Descartes has the great merit that he states facts which any philosophy must fit into its scheme. There are bits of matter, and there are minds. Both matter and mind have to be fitted into the metaphysical scheme.In Whitehead's great work of 400 pages, Process and Reality, we can only sample his thinking, but there is a partial continuity in his jargon with his two previous books. A major novelty is his introduction of a Kantian/Hegelian architectonic of new categories, a single Category of the Ultimate, eight Categories of Existence, twenty-seven Categories of Explanation, and nine Categorial Obligations. He introduces his Categoreal Scheme by defining the four basic notions of the philosophy of organism - an 'actual entity,' that of a 'prehension,' that of a 'nexus,' and that of the 'ontological principle.' Whitehead finds clear antecedents of his thought in Descartes, Leibniz, Locke, Kant, and Plato. This chapter contains an anticipatory sketch of the primary notions which constitute the philosophy of organism. The whole of the subsequent discussion in these lectures has the purpose of rendering this summary intelligible, and of showing that it embodies generic notions inevitably presupposed in our reflective experience—presupposed, but rarely expressed in explicit distinction. Four notions may be singled out from this summary, by reason of the fact that they involve some divergence from antecedent philosophical thought. These notions are, that of an 'actual entity,' that of a 'prehension,' that of a 'nexus,' and that of the 'ontological principle.' Philosophical thought has made for itself difficulties by dealing exclusively in very abstract notions, such as those of mere awareness, mere private sensation, mere emotion, mere purpose, mere appearance, mere causation. These are the ghosts of the old 'faculties,' banished from psychology, but still haunting metaphysics. There can be no 'mere' togetherness of such abstractions. The result is that philosophical discussion is enmeshed in the fallacy of 'misplaced concreteness.'1 In the three notions— actual entity, prehension, nexus—an endeavour has been made to base philosophical thought upon the most concrete elements in our experience.1 Cf. my Science and the Modern World, Ch. III.'Actual entities'—also termed 'actual occasions'—are the final real things of which the world is made up. There is no going behind actual entities to find anything more real. They differ among themselves: God is an actual entity, and so is the most trivial puff of existence in far-off empty space. But, though there are gradations of importance, and diversities of function, yet in the principles which actuality exemplifies all are on the same level. The final facts are, all alike, actual entities; and these actual entities are drops of experience, complex and interdependent.

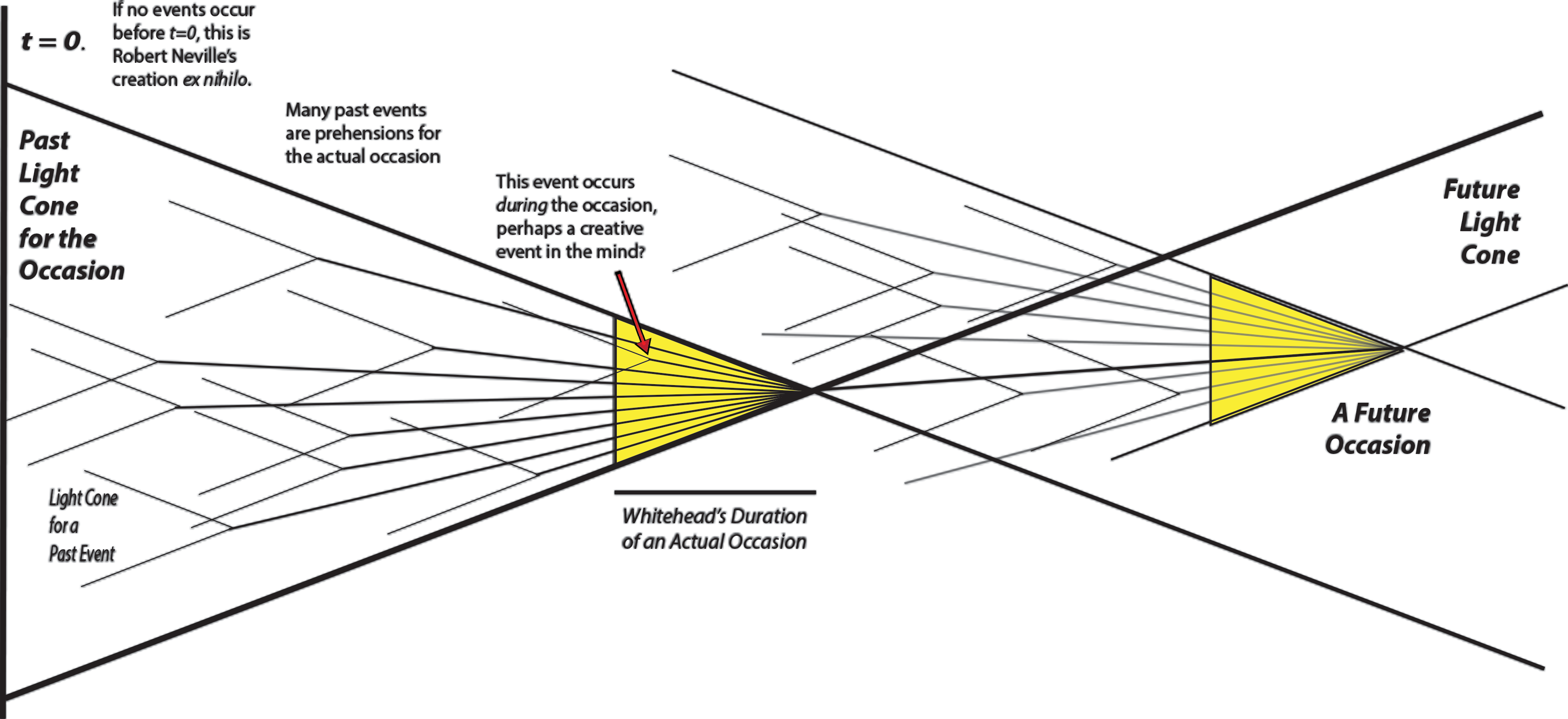
Whitehead on Freedom and Creative Decisions
Whitehead says
The word 'decision' does not here imply conscious judgment, though in some 'decisions' consciousness will be a factor. The word is used in its root sense of a 'cutting off.' The ontological principle declares that every decision is referable to one or more actual entities, because in separation from actual entities there is nothing, merely nonentity—'The rest is silence.' The ontological principle asserts the relativity of decision; whereby every decision expresses the relation of the actual thing, for which a decision is made, to an actual thing by which that decision is made. But 'decision' cannot be construed as a casual adjunct of an actual entity. It constitutes the very meaning of actuality. An actual entity arises from decisions for it, and by its very existence provides decisions for other actual entities which supersede it. Thus the ontological principle is the first stage in constituting a theory embracing the notions of 'actual entity,' 'givenness,' and 'process.' Just as 'potentiality for process' is the meaning of the more general term 'entity,' or 'thing'; so 'decision' is the additional meaning imported by the word 'actual' into the phrase 'actual entity.' 'Actuality' is the decision amid 'potentiality.' It represents stubborn fact which cannot be evaded. The real internal constitution of an actual entity progressively constitutes a decision conditioning the creativity which transcends that actuality.Whitehead's ninth Categoreal Obligation is the very important Category of Freedom and Determination, which he finds discussed in Locke and Immanuel Kant. Whitehead says the concrescence of each individual actual entity is internally determined and externally free. This category can be condensed into the formula, that in each concrescence whatever is determinable is determined, but that there is always a remainder for the decision of the subject-superject of that concrescence. This subject-superject is the universe in that synthesis, and beyond it there is nonentity. This final decision is the reaction of the unity of the whole to its own intemal determination. This reaction is the final modification of emotion, appreciation, and purpose. But the decision of the whole arises out of the determination of the parts, so as to be strictly relevant to it.Isabelle Stengers analyzed Whitehead's idea of a "decision" in an actual occasion. At the end of Part One of her Thinking with Whitehead, Stengers notes that an "actual occasion" contains multiple incoming prehensions from past occasions which Whitehead calls "alternative suggestions." These she identifies with William James's alternative possibilities, which is the basis of two-stage models of free will. Stengers quotes this fragment from Science and the Modern World. every actual occasion is set within a realm of alternative interconnected entities. This realm is disclosed by all the untrue propositions which can be predicated significantly of that occasion. It is the realm of alternative suggestions, whose foothold in actuality transcends each actual occasion. The real relevance of untrue propositions for each actual occasion is disclosed by art, romance, and by criticism in reference to ideals. It is the foundation of the metaphysical position which I am maintaining that the understanding of actuality requires a reference to ideality. The two realms are intrinsically inherent in the total metaphysical situation. The truth that some proposition respecting an actual occasion is untrue may express the vital truth as to the aesthetic achievement. It expresses the ‘great refusal’ which is its primary characteristic. An event is decisive in proportion to the importance (for it) of its untrue propositions:Stengers' analysis contains echoes of the great existentialists' notions that any "decision" involves the "destruction" of some alternative possibilities condemning them to "non-being." For example, Jean-Paul Sartre's L'être et le néant. Then Stengers homes in on James' notion of "doing otherwise as the essence of a free decision." Sometimes, in the course of this text, I have been unable not to anticipate, and to use the word "decision," which Whitehead was to use in Process and Reality to name the "breaking off" that turns the occasion into the affirmation of a "thus and not otherwise." When he named the "great refusal," Whitehead himself could doubtless not help but be inhabited by a syntax that makes the occasion the producer of its limitation. No doubt he was aware, when writing Science and the Modern World, that his concept of an occasion was merely a first approximation. And perhaps the use of the word "decision," in Process and Reality, indicates that he has henceforth provided himself with the means to fully affirm the meaning William James conferred upon this term: that of a living moment that produces its own reasons. Decisions, for him who makes them, are altogether peculiar psychic facts. Self-luminous and self-justifying at the living moment at which they occur, they appeal to no outside moment to put its stamp upon them or make them continuous with the rest of nature. Themselves it is rather who seem to make nature continuous; and in their strange and intense function of granting consent to one possibility and withholding it from another, to transform an equivocal and double future into an inalterable and simple past (DD, 158). With James, Whitehead refused to make continuity primary; that is, he also refused to allow the occasion to be deduced from the whole. Every continuity is a result, a succession of resumptions that are so many "purposes," deciding the way the present will prolong the past, give a future to this past and make it "its" past. Yet the way James characterizes decision, "granting consent to one possibility and withholding it from another," could not be adopted as such, for it contains too many unknowns. It had to be constructed, in a way that enables every production of existence to be characterized as a decision. It is the actual occasions themselves that will affirm, no longer merely "just this, and no more," but "thus and not otherwise."Continuity is the essential nature of field theories, with their infinite number of points on a line. Whitehead's atomicity of experience suggests he favors a particulate view of nature, with a finite number of actual entities? In his Chapter X on Process, Whitehead again tells us that some of his most important concepts about process come from John Locke. The clear talk about Locke devolves into obscure Whitehead jargon. [T]here are two kinds of fluency. One kind is the concrescence which, in Locke's language, is 'the real internal constitution of a particular existent.' The other kind is the transition from particular existent to particular existent. This transition, again in Locke's language, is the 'perpetually perishing' which is one aspect of the notion of time; and in another aspect the transition is the origination of the present in conformity with the 'power' of the past. The phrase 'the real internal constitution of a particular existent,' the description of the human understanding as a process of reflection upon data, the phrase 'perpetually perishing,' and the word 'power' together with its elucidation are all to be found in Locke's Essay. Yet owing to the limited scope of his investigation Locke did not generalize or put his scattered ideas together. This implicit notion of the two kinds of flux finds further unconscious illustration in Hume. It is all but explicit in Kant, though—as I think—misdescribed. Finally, it is lost in the evolutionary monism of Hegel and of his derivative schools. With all his inconsistencies, Locke is the philosopher to whom it is most useful to recur, when we desire to make explicit the discovery of the two kinds of fluency, required for the description of the fluent world. One kind is the fluency inherent in the constitution of the particular existent. This kind I have called 'concrescence.' The other kind is the fluency whereby the perishing of the process, on the completion of the particular existent, constitutes that existent as an original element in the constitutions of other particular existents elicited by repetitions of process. This kind I have called 'transition.' Concrescence moves towards its final cause, which is its subjective aim; transition is the vehicle of the efficient cause, which is the immortal past. The discussion of how the actual particular occasions become original elements for a new creation is termed the theory of objectification. The objectified particular occasions together have the unity of a datum for the creative concrescence. But in acquiring this measure of connection, their inherent presuppositions of each other eliminate certain elements in their constitutions, and elicit into relevance other elements. Thus objectification is an operation of mutually adjusted abstraction, or elimination, whereby the many occasions of the actual world become one complex datum. This fact of the elimination by reason of synthesis is sometimes termed the perspective of the actual world from the standpoint of that concrescence. Each actual occasion defines its own actual world from which it originates. No two occasions can have identical actual worlds.
The Function of Reason
In his 1929 book, Whitehead speculated about the ability of biological evolution to escape the destructive tendency of the second law of thermodynamics.
History discloses two main tendencies in the course of events. One tendency is exemplified in the slow decay of physical nature. With stealthy inevitableness, there is degradation of energy. The sources of activity sink downward and downward. Their very matter wastes. The other tendency is exemplified by the yearly renewal of nature in the spring, and by the upward course of biological evolution.Whitehead here is asking the same question as his scientist colleague Arthur Stanley Eddington asked in his own Gifford Lectures of 1928, published as The Nature of the Physical World. This is our fundamental question of information philosophy, "How exactly has the universe escaped from the total disorder of thermodynamic equilibrium and produced a world full of information?" The answer is the cosmic creation process that Whitehead anticipated as "some general counter-agency." The material universe has contained in itself, and perhaps still contains, some mysterious impulse for its energy to run upwards. This impulse is veiled from our observation, so far as concerns its general operation. But there must have been some epoch in which the dominant trend was the formation of protons, electrons, molecules, and stars. Today, so far as our observations go, they are decaying. We know more of the animal body, through the medium of our personal experience. In the animal body, we can observe the appetition towards the upward trend, with Reason as the selective agency. In the general physical universe we cannot obtain any direct knowledge of the corresponding agency by which it attained its present stage of available energy... The universe, as construed solely in terms of the efficient causation of purely physical interconnections, presents a sheer, insoluble contradiction... The moral to be drawn from the general survey of the physical universe with its operations viewed in terms of purely physical laws, and neglected so far as they are inexpressible in such terms, is that we have omitted some general counter-agency.Whitehead hopes to discover some underlying "purpose," which he sees clearly present in biological evolution as "foresight" and "intention." He describes the function of "Reason" as the promotion of "the art of life." (p.4) And he says "At the lower end of the scale, it is hazardous to draw any sharp distinction between living things and inorganic matter." (p.5) This will open the way to his panpsychist view of a "mysterious impulse" behind energy. Reason is the organ of emphasis upon novelty. It provides the judgment by which realization in idea obtains the emphasis by which it passes into realization in purpose, and thence its realization in fact. (ibid., p.20) Provided that we admit the category of final causation, we can consistently define the primary function of Reason. This function is to constitute, emphasize, and criticize the final causes and strength of aims directed towards them. The pragmatic doctrine must accept this definition. It is obvious that pragmatism is nonsense apart from final causation. (ibid., p.26) )Following Kant, Whitehead distinguishes between practical and speculative Reason, the latter being the systematic philosophy of the early Greeks. the critical discovery which gave to the speculative Reason its supreme importance was made by the Greeks. Their discovery of mathematics and of logic introduced method into speculation. Reason was now armed with an objective test and with a method of progress. In this way Reason was freed from its sole dependence on mystic vision and fanciful suggestion. (ibid., p.40)We can note in passing that Whitehead is not what Kant called an "onto-theologist," one who hopes to discover God by thinking about the concept of "Being," the "Boundless", the "Indeterminate," etc. Whitehead was what Kant called a "cosmo-theologist," one who tries to discern God through our experiences with the natural world.
Whitehead and Information Philosophy
There are some broad similarities between information philosophy and Whitehead's "philosophy of organism" or his oddly named "organic mechanism." To see the connection, we must sharpen the idea of Newtonian mechanism and even the deterministic motions of matter in special relativity. These both seem well-described by Whitehead's attack on "simple location."
Today we describe this as "reductionism," the mistaken idea that all phenomena are reducible to physics and chemistry, that biological organisms and even mental phenomena are reducible to the motions of their constituent material particles.
Reductionism claims that there are deterministic causal chains coming "bottom up" from matter. If there are "mental phenomena," they are merely "epiphenomena," giving us the illusion of mental events and "mental causation."
Whitehead thought relativity and quantum mechanics had added something new to mechanical materialism. He was wrong about relativity, but right about quantum physics, though he did not understand what it is that quantum phenomena add to biological organisms and mental processes. And he did not see the importance of another physical process that his British colleague Arthur Stanley Eddington called attention to, the second law of thermodynamics, in his Gifford Lectures the same year as those of Whitehead.
Perhaps the greatest similarity between I-Phi and Process Philosophy is that they both claim to explain a "creative process," which lies behind the "emergence of "purpose" (the entelechy of Aristotle or the teleonomy of Colin Pittendrigh and Jacques Monod) in living things.
Quantum Whiteheadians
A number of scholars argue that Whitehead's panpsychism can explain some puzzling aspects of quantum mechanics, including Henry P. Stapp, Stuart Hameroff, Ulrich Mohrhoff, Harald Atmanspacher, and Massimo Pauri, among many others.
Glossary of Key Terms used by Alfred North Whitehead
Also see our I-Phi glossary of terms related to problems of freedom, value, and knowledge uses hyperlinks (with blue underlines) to provide recursive definitions from within each entry.
Hyperlinks go to relevant pages in the I-Phi website and to external sites such as the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, where available.
Click on the "Search I-Phi" link to find all the webpages on the I-Phi website that refer to the given term. And click on "I-Phi Page" to get a much more detailed description of the term.
A
Actual_Entity is initially Whitehead's term for the classic term "substance." Later it is mostly replaced by an Actual Occasion.
"'Actual entities' - also termed 'actual occasions' - are the final real things of which the world is made up...God is an actual entity."(PR18) "The term 'actual occasion will always exclude God from its scope." (PR88)
"The real internal constitution of an actual entity progressively constitutes a decision conditioning the creativity which transcends that actuality." (PR230)
Other glosses - Actual Occasion, Concrescence, Consequent, Creativity, Duration,Ground, Many, Process, Prehension, Subject, SuperjectTransition, Simple Location
"An actual occasion is a prehension of one infinite hierarchy (its associated hierarchy) together with various finite hirerarchies." (SMW 171).
Other glosses - Abstraction, Actual Entity, Apprehension, Concrescence, Consequent, Creativity, Duration, Eternal Object, Experience, Ingression, Ground, Many, Mental Occasion, Nexus, One, Organic Mechanism, Organism, Ontological Principle, Perishing, Process, Prehension, Satisfaction, Subject, Superject, Transition, Simple Location, Valuation
Grasping an idea or concept with the intellect or as a cognitive act. Whitehead contrasts the term prehension, which he defines as the immediate grasping of perception without cognition or intellection.
Other glosses - Prehension
Concrescence is the growing together of many prehensions or grounds (both called ingressions) into one consequent.
"To be causa sui means that the process of concrescence is its own reason for the decision in respect to the qualitative clothing of feelings...The freedom inherent in the universe is constituted by this element of self-causation. (PR88)
"Locke is the philosopher to whom it is most useful to recur, when we desire to make explicit the discovery of the two kinds of fluency, required for the description of the fluent world. This kind I have called 'concrescence.' The other kind is the fluency the perishing of the process, on the completion of the particular existent, constitutes that existent as an original element in the constitutions of other particular existents elicited by repetitions of process. This kind I have called 'transition.' Concrescence moves towards its final cause, which is its subjective aim; transition is the vehicle of the efficient cause, which is the immortal past."
Other glosses - Actual_Entity, Actual Occasion, Consequent, Creativity, Duration, Ingression, Ground, Many, Nexus, One,Organism, Ontological Principle, Perishing, Process, Prehension, Transition
Creativity is the result of a Process, an Actual Occasion. It starts with one or more Prehensions or perceptions of the Many that Transition into the Concrescence of a new Unity, a One that Perishes as it forms a part of a new Many.
Creativity, the Many, and the One are the three parts of the "Category of the Ultimate."
Other glosses - Actual Occasion, Concrescence, Many, One, <Perishing, Prehension, Process, Transition
An Actual Occasion cannot be an infinitesimal moment in time if it is to be perceived and prehended. That notion of an atomic amount of time is the duration.
An Ideal Entity is an ideal or Abstract Form.
Whitehead adapts the idea of a physical event, an infinitesimal point in relativistic space and time to his notion of what we Perceive or Prehend, which is a substantial volume in space and duration in time. In his later writing, these Events become his Actual Occasions.
Other glosses - Abstraction, Actual Entity, Actual Occasion, Apprehension, Concrescence, Consequent, Creativity, Duration, Eternal Object, Experience, Ingression, Ground, Many, Mental Occasion, Nexus, One, Organic Mechanism, Organism, Ontological Principle, Perishing, Process, Prehension, Satisfaction, Subject, Superject, Transition, Simple Location, Valuation
An Eternal Object
An Eternal Object is an immaterial Form or Idea that exists outside of space and time. The Platonic Forms, logical truths, and the mathematical entities in his Principia Mathematica are Eternal Objects. They are pure potential that can be realized in an Actual Entity. All Objects can be Perceived and Felt by Subjects.
Other glosses - Abstraction, Actual_Entity, Actual Occasion, Apprehension, Concrescence, Consequent, Creativity, Duration, Eternal Object, Experience, Ingression, Ground, Many, Mental Occasion, Nexus, One, Organic Mechanism, Organism, Ontological Principle, Perishing, Process, Prehension, Satisfaction, Subject, Superject, Transition, Simple Location, Valuation
Whitehead talks of many kinds of Experience - Aesthetic, Higher and Lower, Immediate, and especially Religious Experience.
Other glosses - Abstraction, Actual_Entity, Actual Occasion, Apprehension, Concrescence, Consequent, Creativity, Duration, Eternal Object, Experience, Ingression, Ground, Many, Mental Occasion, Nexus, One, Organic Mechanism, Organism, Ontological Principle, Perishing, Process, Prehension, Satisfaction, Subject, Superject, Transition, Simple Location, Valuation
Before he turned to philosophy at Harvard, Whitehead had expanded the idea of a physical event at an infinitesimal point in space and time to something with more spatial extension and temporal duration, so events could overlap.
A Ground is one of the Many prior Actual Occasions as Prehensions as Ingressions in the Transition and Concrescence to a new Actual Occasion or Consequent One, which Perishes.
Other glosses - Actual_Entity, Actual Occasion, Concrescence, Consequent, Ingression, Ground, Many, One, Perishing, Process, Prehension
To be Indeterminate is to say that at least some of the many properties of an Entity are unknown, perhaps unknowable.
Other glosses - Actual Entity
Ingression is how earlier Occasions and Eternal Objects enter into the Creativity and Concrescence, perishing in the Transition to a new Actual Occasion (the Consequent) .
An Actual Occasion is a Microscopic process, larger and longer than the infinitesimal point in ordinary space-time, but much smaller than tables and chairs, for example.
Macroscopic processes are made up of multiple occasions in a Nexus or society of occasions
A Microscopic process of Concrescence is one that is not temporal. Here the "earlier" Prehensions are only logical, not actual, preconditions for the Occasion.
Other glosses - Actual Occasion, Nexus
A Nexus is a complex of multiple Occasions. The Actual World consists of many Nexūs (plural).
What many philosophers call “actual entities,” Whitehead calls “nexūs.” This is most obvious
in relation to philosophies that stay close to ordinary language and treat the objects of everyday experience as actual entities. Many process philosophers take Events as primary, though for Whitehead, most Events are Nexūs, multiple actual occasions.
Whitehead sometimes describes multiple Nexūs as Societies.
Other glosses - Actual Occasion
Occasion is Whitehead's fundamental name for what goes on in a finite (or atomic) volume in space and a duration in time, not the infinitesimal point associated with an "event" in the Minkowski-Einstein "block universe," which Whitehead calls a "simple location."
An occasion may be something material happening in nature, or something mental happening in a mind.
Occasions function as Causes to its successor Occasions, which are affected by it as the Ingression of Prehensions.
Whitehead often describes occasions with other terms, such as Actual Entities, Creatures, Concretions,
Whitehead's Ontological Principle is that only Actual Entities contribute causally to events. His "Eternal Objects" play no causal role because they are immaterial, e.g., the Platonic Forms. Information Philosophy shows how immaterial ideas in minds, a subset of communications in biology, in fact play a causal role in the world.
For Whitehead, every entity is considered to be an organism. This is a fundamental error. Organisms are biological entities. They maintain themselves against breakdown by the second law of thermodynamics, using negative entropy streams from the sun that flow through all earthly life. Organisms are creative, evolving according to the neo-Darwinian synthesis.
Organisms are Forms through which Matter and Energy continuously flow.
And it is information communications and processing that controls those flows, using negative entropy that flows from the sun to all life.
Organic Mechanism is Whitehead's early term for what later is called Organism
Other glosses - Organism
For Whitehead, every entity is considered to be an organism. This is his fundamental error. Organisms are biological entities. They maintain themselves against breakdown by the second law of thermodynamics, using negative entropy streams from the sun that flow through all earthly life. Organisms are creative, evolving according to the neo-Darwinian synthesis.
Other glosses - Organic Mechanism
Panpsychism is Whitehead's attempt to avoid a "bifurcation" between the organic and inorganic world.. But when he applies his ideas that describe mental events like perception, experience, valuations, etc. all the way down to material particles, he mistakenly introduces panpsychism, the idea that even the most elementary material particles also have minds.
Whitehead describes the physical processes of matter in space and time using terms that are only appropriate for biological entities, like perception, decision, valuation, etc. He transforms an entirely material space-time "event" into an "occasion" with mental properties. But saying such a thing does not make it so, even if Whitehead says that God is overseeing the process.
By contrast, the information philosophy emphasis on the creation of information structures distinguishes the creation of passive structures like the galaxies, stars, planets, even elementary material particles, from active information structures that communicate information among their parts and to and from other active structures to form a community of living things (something like Whitehead's "nexūs" or "societies").
For information philosophy, an organism is a form through which matter and energy flow, and information processes manage those flows. For passive information structures like elementary particles, as well as the galaxies, stars, and planets, matter and energy flows are controlled entirely by natural forces like gravity, electromagnetism, and nuclear forces.
Other glosses - Abstraction, Actual_Entity, Actual Occasion, Apprehension, Concrescence, Consequent, Creativity, Duration, Eternal Object, Experience, Ingression, Ground, Many, Mental Occasion, Nexus, One, Organic Mechanism, Organism, Ontological Principle, Perishing, Process, Prehension, Satisfaction, Subject, Superject, Transition, Simple Location, Valuation
Prehension is a non-cognitive version of an Apprehension. It is the immediate "grasping" or perception (e.g., a Humean "impression") of an idea before the mental mediation in terms of concepts.
Physical prehensions are perceptions of actual entities or actual occasions. Conceptual prehensions are "ingressions" of eternal objects.
Prehensions are the first stage (the Many Grounds) which grow together in the Concrescence that results in a Consequent One
Other glosses - Actual Entity, Actual Occasion, Concrescence, Consequent, Eternal Object, Ingression, Ground
Whitehead's Process puts the emphasis on things happening (Actual Occasions) that are far more than the Simple Locations and Paths of material particles in the universe.
Other glosses - Abstraction, Actual_Entity, Actual Occasion, Apprehension, Concrescence, Consequent, Creativity, Duration, Eternal Object, Experience, Ingression, Ground, Many, Mental Occasion, Nexus, One, Organic Mechanism, Organism, Ontological Principle, Perishing, Process, Prehension, Satisfaction, Subject, Superject, Transition, Simple Location, Valuation
Satisfaction suggests that the Actual Occasion has feelings following the Concrescence (the Consequent), even if it is a purely material event.
"The actual entity terminates its becoming in one complex feeling involving a completely determinate bond with every item of the universe, the bond being either a positive or a negative prehension." (PR71) The 'satisfaction' is the 'superject' of rather than the 'substance' or the 'subject.' (PR227)
Simple Location is the path in space and time of a bit of matter, but that neglects its relations with all the other bits of matter and other Actual Occasions in a Process.
The standard theory of relativity regards the path of a particle as a succession of events. Whitehead's relativity includes the relations with every other event in the universe.
Other glosses - Actual Occasion, Process
For Whitehead, Subjects Perceive or Prehend Objects, including themselves as Subjects, as Actual Occasions, as Experiences. In an Ideal World, Objects only exist for Subjects. Subjects exist for themselves.
Other glosses - Actual Occasion, Apprehension, Concrescence, Consequent, Creativity, Duration, Eternal Object, Experience, Ingression, Ground, Organism, Process, Prehension, Superject, Transition, Valuation
Although Whitehead often views an Actual Occasion as a Subject, he sometimes describes the Occasion as the Superject of its Prehensions.
"An actual entity is to be conceived both as a subject presiding over its own immediacy of becoming, and a superject which is the atomic creature exercising its function of objective immortality." (PR71)
Other glosses - Actual Occasion, Concrescence, Consequent, Creativity, Duration, Eternal Object, Ingression, Ground, Many, Nexus, One, Organic Mechanism, Organism, Ontological Principle, Perishing, Process, Prehension, Subject, Transition
Transition is still another term for a Macroscopic process, which involves the temporal “transition” from earlier Prehensions
Occasions, functioning as Causes to its successors, which are affected by it.
By comparison, there is no temporal Transition in Microscopic process of Concrescence. Here the "earlier" Prehensions are only logical preconditions for the Occasion, viz. Eternal Objects
Other glosses - Actual Occasion, Creativity, Duration, Eternal Object, Experience, Ground, Many, Mental Occasion, Nexus, One, Organic Mechanism, Organism, Ontological Principle, Perishing, Process, Prehension, Valuation
Every Actual Occasion is a Creation, and a Valuation
Other glosses - Actual Occasion, Creativity, Duration, Eternal Object, Experience, Ingression, Organism, Ontological Principle, Perishing, Process, Prehension, Satisfaction
References
John B. Cobb, Jr's Whitehead Word Book,
Randall Auxier's Glossary for Religion in the Making 1996, Donald Sherburne's Glossary for his Key to Whitehead's Process and Reality.
For Teachers
For Scholars
Some other online glossaries of Whitehead terms:
|